A ballooning or bulge in a brain’s blood vessel is called a brain aneurysm. Sometimes, the condition is called cerebral aneurysm or intracranial aneurysm. In most cases, an aneurysm looks like a berry that hangs on a stem.
Aneurysms may break and cause bleeding between the brain and its coverings. In such cases, the disease is called a subarachnoid hemorrhage, which is a type of hemorrhagic stroke.
While brain aneurysms are common, most of them are not dangerous, especially small ones. Furthermore, most aneurysms do not rupture and do not cause any symptoms or health problems. Physicians usually found these aneurysms during tests done for another condition. However, a ruptured aneurysm is considered a medical emergency and may lead to death without immediate treatment.
For people with aneurysms that have not ruptured, treatment may help prevent ruptures in the future. Discuss with your healthcare professional for more details.
Brain Aneurysm Types
- Saccular aneurysm (also known as berry aneurysm) – In such cases, the aneurysm looks like a berry (a round and blood-filled sac that protrudes from the primary artery). This is the most common aneurysm type and it often appears from the arteries at the brain’s base.
- Fusiform aneurysm – This type leads to bulging of all artery sides.
- Mycotic aneurysm – This often occurs due to an infection that negatively affects the arteries of the brain. Therefore, it may weaken the artery wall, which allows an aneurysm to form.
Symptoms
If the aneurysm has not ruptured, it commonly does not cause symptoms. In any case, a ruptured one is a life-threatening condition that 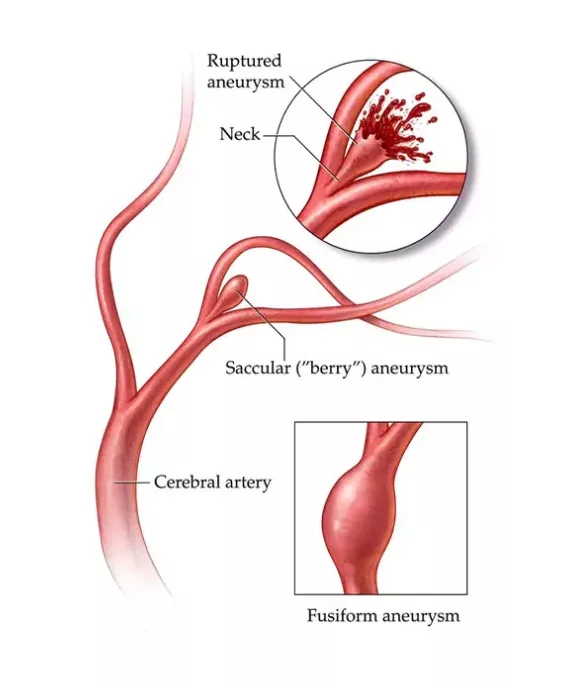 requires immediate treatment. Check below some symptoms:
requires immediate treatment. Check below some symptoms:
Ruptured Aneurysm
The primary symptom of a ruptured aneurysm is a sudden severe headache. Commonly, when it occurs, people describe it as the worst headache they ever had. Check below other symptoms of a ruptured aneurysm:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Dropping eyelids
- Loss of consciousness
- Confusion
- Light sensitivity
- Vision changes (including double or blurred vision)
- Neck stiffness
- Seizures
Leaking Aneurysm
Sometimes, aneurysms may leak small amounts of blood. In most cases, when leaking aneurysms occur, a more severe rupture usually happens. Aneurysm leakage may occur for days or even weeks before a rupture. A leaking aneurysm usually causes sudden and severe headaches that often last between a few days and up to two weeks.
Unruptured Aneurysm
Sometimes, even an unruptured aneurysm may cause symptoms because it puts pressure on the brain and nearby nerves, especially if it is large. Check below some symptoms:
- Dilated pupils
- Eye pain
- Vision changes (such as double vision)
- Numbness that often happens in one face side
It is advised to seek emergency care if sudden and severe headaches occur.
Causes
This condition happens because of the artery wall thinning. It forms at branches or forks in the arteries of those areas where they are weaker. While it may occur anywhere in the brain, it mostly appears in the arteries at the brain’s base.
Risk Factors
There are multiple factors that may cause artery walls to become weakened. Thus, they increase the risk of developing aneurysms. While most factors that increase the risk of brain aneurysms develop over time, there are some congenital diseases that significantly increase the risk of this disease. Check below some examples:
- Age – This condition may happen at any age, but is mostly diagnosed in people between 30 and 60 years old.
- Sex – Brain aneurysms occur more frequently in females than males.
- Smoking – People who smoke are at increased risk of brain aneurysms and their rupture.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) – This condition causes the artery walls to weaken. As a result, it allows an aneurysm to form.
- Illegal drug use – These drugs increase your blood pressure. However, those who administer them intravenously (IV) may get an infection that causes mycotic aneurysms.
- Heavy alcohol use – Those who drink large amounts of alcohol may develop hypertension, which is a risk factor for brain aneurysms.
- Inherited connective tissue disorders – One of them is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which causes the artery walls to weaken.
- Polycystic kidney disease – This is an inherited disease that causes fluid-filled sacs in the kidneys. This condition may cause high blood pressure.
- Coarctation of the aorta (a narrow aorta) – Aorta is the major blood vessel that delivers oxygen-rich blood from the heart throughout the body.
- Brain AVM (arteriovenous malformation) – In such cases, blood vessels (including veins and arteries) of the brain are tangled, which negatively affects blood flow.
Family History of a Brain Aneurysm
Your risk of developing a brain aneurysm increases significantly if you have a blood relative who has the disease. These include a parent, brother, sister, or child. Discuss with your healthcare professional about regular screening if you are at increased risk of developing it.
Some people may develop a brain aneurysm after a head injury.
Factors that may Increase the Risk for a Ruptured Aneurysm
Check below for additional factors that may increase your risk of a ruptured aneurysm:
- Large aneurysms
- Smoking cigarettes
- Hypertension that is not treated
What Are The Potential Complications of Brain Aneurysm?
You may wonder what happens if this disease is left untreated. An untreated brain aneurysm may lead to certain unpleasant and even life-threatening complications. Check some complications below:
- Recurrent bleeding – If an aneurysm leaks or is ruptured it may lead to bleeding that causes damage to the brain cells.
- Vasospasm – This complication occurs when the brain’s blood vessels become narrowed due to a ruptured aneurysm. Therefore, it may lead to ischemic stroke and additional damage to the brain cells.
- Hydrocephalus (fluid buildup within the brain) – This condition happens due to a ruptured aneurysm that happens between the brain and its covering tissues. As a result, it blocks the fluid that moves around the brain and spinal cord.
- Sodium level changes – Bleeding may cause imbalances in sodium levels. Hence, it may lead to brain cell swelling and permanent damage.
How to Prevent Brain Aneurysm?
Unfortunately, usually, it is not possible to prevent brain aneurysms. However, you can consider some of the following tips to reduce the risk. These include quitting smoking, limiting or avoiding alcoholic drinks and illegal drugs (such as cocaine), and managing high blood pressure.
Diagnosis
While the main symptom of a ruptured aneurysm is sudden and severe headaches, it requires testing to confirm the condition. The following tests are used to confirm the disease and exclude others that cause similar symptoms. For example:
- CT (computerized tomography) scan – This test uses X-rays to make images of the brain. It may identify stroke, bleeding in the brain, and other problems. To get more detailed images, physicians may inject a specific dye into the bloodstream.
- Lumbar puncture (also called a spinal tap) – This test is often used when doctors suspect a subarachnoid hemorrhage. During this procedure, doctors will take a small sample of cerebrospinal fluid for testing.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan – This imaging test is used to get more detailed images of the brain. It also may identify the exact size, shape, and location of aneurysms.
- Cerebral angiogram – This procedure involves a catheter (a long and flexible tube) that is inserted in a blood vessel usually in the wrist or groin and then guided to the brain’s blood vessels. Thereafter, a special dye is injected into the blood vessels that helps identify aneurysms on further X-rays.
Treatment
To repair a ruptured aneurysm, doctors often recommend surgery or endovascular treatment. The procedure in which the aneurysm is treated from the inside of the artery is called endovascular treatment.
Surgery
There are two primary treatments to repair a ruptured brain aneurysm. Sometimes, the following surgeries may be used for people with unruptured aneurysms, but the risks may outweigh the benefits.
Surgical Clipping
This procedure is used to close an aneurysm. Surgeons will remove the section of your skull to reach the aneurysm. They also locate the blood vessels and supply the aneurysm with blood. Thereafter, surgeons will place a small metal clip on the aneurysm neck to interrupt blood flow into it.
Generally, this is an effective treatment because aneurysms do not return once are treated with surgical clipping. However, this surgery like many others carries some risks including bleeding in the brain, reduced blood flow to the brain, and others.
People usually recover from this surgery within 4-6 weeks.
Endovascular Coiling
This treatment is less invasive and involves a catheter that is inserted into a major blood vessel and then guided to the brain arteries. Thereafter, they will place a coil or stent into the aneurysm.
- Endovascular coils – This treatment involves a spiral-shaped coil that is placed inside the aneurysm. Therefore, it prevents blood flow to the aneurysm and may cause blood clots in the aneurysm that help destroy it.
- Endovascular stents – This is a small tube that is usually used to hold the coil in place. It is used for certain aneurysm types only.
Additional Treatments
Doctors may prescribe additional medicines for people with ruptured brain aneurysms to lessen the symptoms and manage complications. For example:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers – For example Acetaminophen
- Calcium channel blockers – These medications are used to prevent calcium from entering blood vessel walls to prevent vasospasm. Physicians usually prescribe Nimodipine.
- Vasodilators – These medications are usually given to the patients intravenously (IV) to open blood vessels. It helps to prevent strokes.
- Angioplasty – This procedure is used to widen narrowed blood vessels in the brain.
- Anti-seizure medications
- Ventricular or lumbar draining catheters and shunt surgery – These procedures are used to prevent fluid buildup after a ruptured aneurysm.
- Rehabilitative therapy – Sometimes, people need physical, occupational, and speech therapy after brain damage caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Home Remedies
The following tips may help reduce the risk of developing brain aneurysms. For example:
- Quit smoking or never begin
- Control your blood pressure
- Adopt a healthy diet full of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Do not use illegal drugs (such as cocaine, methamphetamine, and others)
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary symptoms of a brain aneurysm?
These include:
- A drooping eyelid
- Speaking difficulties
- Weakness
- Numbness
- Headaches
- Eye pain
- Blurred or double vision
How common is death from brain aneurysm?
Approximately 50% of people with a ruptured brain aneurysm die. However, those who survive experience permanent neurological damage. That’s why it is considered a medical emergency that requires immediate treatment.
What are the potential brain aneurysm complications?
- Vasospasms
- Recurrent bleeding
- Hydrocephalus
- Sodium level changes
- Hyponatremia
- Epilepsy
- Frontal lobe syndrome
This document does not contain a complete list of brain aneurysm complications. Ask your healthcare professional if you have additional questions.