A type of irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) and the most common type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is called atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia (AVNRT). Usually, people with this condition have a fast heart rate that begins and stops suddenly. Those who suffer from AVNRT often have a heart rate of more than 100 beats per minute. Mostly, this type of arrhythmia happens due to changes in the heart signaling.
While anyone may develop this condition, it mostly occurs in young women. In mild cases, people with this condition do not need treatment. In more advanced forms of AVNRT, doctors often prescribe specific actions or movements, medications, or heart procedures.
Symptoms
One of the most common symptoms of atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia is very fast heartbeats. It often ranges between 120 to 280 beats per minute. While not everyone who suffers from AVNRT experiences symptoms, they may include the following ones. For example:
- A pounding feeling in the neck
- Chest tightness, pressure, or pain
- Dizziness
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Increased sweating
- Fluttering or pounding heartbeats (also known as palpitations)
- Weakness
- Fatigue (extreme tiredness)
- Fainting
You should see a doctor if any of the following symptoms occur. Examples include:
- Unexplained changes in the heartbeat
- Abnormal fast heart rate
- Changes in feeding
- Skin color changes
- Sweating without reason
Go to the nearest emergency room or call 911 in the U.S. if you experience the following symptoms. For example:
- Difficulty breathing
- Weakness
- Dizziness
- Sudden chest pain (this is also a symptom of myocardial infarction)
Causes
Certain changes in the electrical signals that control the heartbeat usually cause this condition. Normally, the electrical signals follow a specific pathway, but in people with AVNRT, there is an additional signaling pathway (also known as a reentrant circuit). This additional pathway makes the heart muscle beat too early, which prevents the heart from pumping blood as it should.
Sometimes, physicians do not fully understand why people have this additional pathway that causes the disease. Experts think some heart structure changes may lead to it.
Risk Factors
This condition happens mostly in young women, but it may develop in everyone. Furthermore, doctors have identified some factors that could increase your risk of developing AVNRT. For example:
- Heart disease (including heart valve disease, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and others)
- Congenital heart defects (heart conditions present at birth)
- Previous heart, lung, or throat surgery
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Thyroid disease
- Lung diseases (including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or COPD)
- Unmanaged diabetes
- Certain medicines, like those used to treat allergies, colds, and asthma
Additional Risk Factors
These include:
- Smoking
- Caffeine
- Emotional distress
- Misuse of alcoholic drinks (more than 15 drinks per week for men and more than 8 drinks a week for women)
- Stimulant drugs (such as methamphetamine, cocaine, and others)
What Are The Potential Complications of AVNRT?
People with this condition may also experience some complications, especially if they do not get treatment. Check below some examples:
- Worsening of the existing health conditions
- Sudden cardiac arrest (sudden stop of the heart activity)
- Confusion
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Shock
This article does not contain all possible complications of atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia. For more details, discuss it with your healthcare professional.
Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals usually diagnose this condition by asking questions about the symptoms and medical history and listening to your heart and lungs with a stethoscope. They may also perform some tests to confirm the condition and exclude others that cause similar symptoms. Check below some tests often involved in AVNRT diagnosis:
- Blood tests – These tests are used to check for thyroid disease and other conditions that contribute to irregular heart rate.
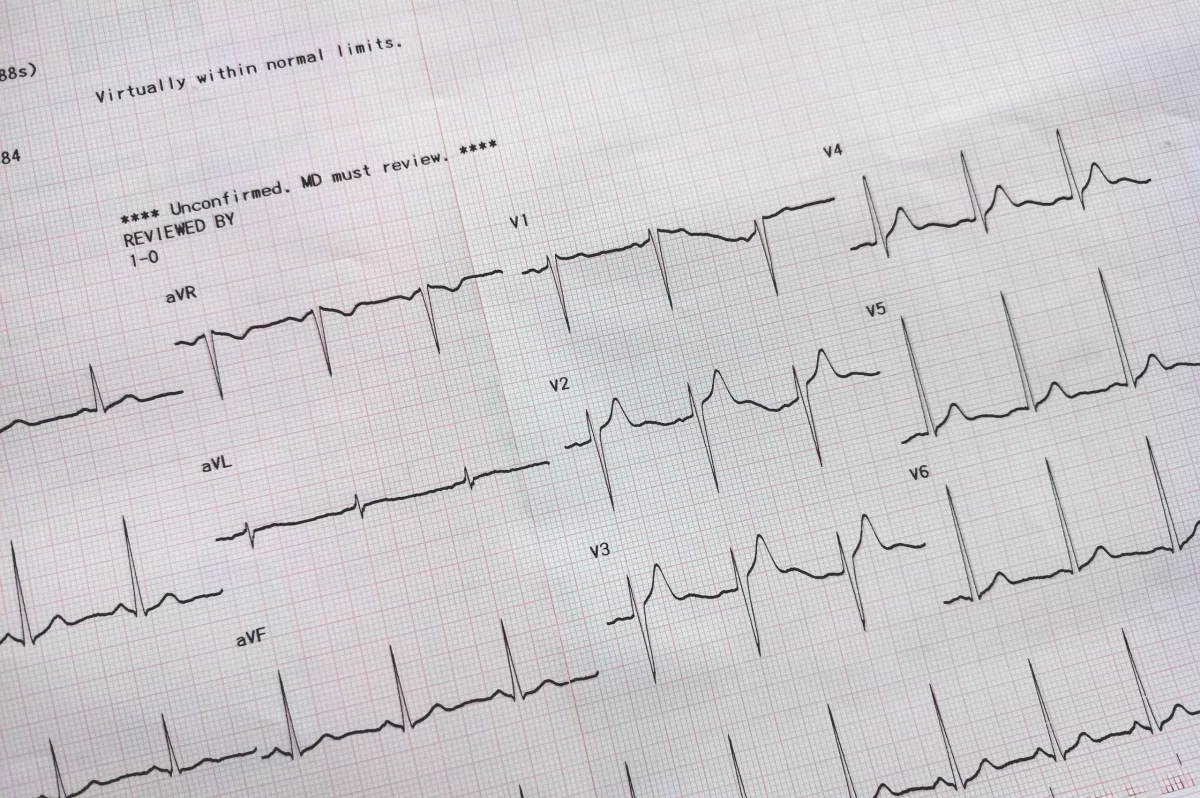
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) – This is a quick and painless test used to measure the electrical activity of the heart.
- Holter monitor – This is a small device used to record the heart’s activity during the day. It is often worn for 2-3 days.
- Echocardiogram – This test uses sound waves to make pictures of the heart. It shows the size of the heart muscle and how blood flows through it.
- Exercise stress test – During this procedure, doctors will check your heart while walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bike.
- Electrophysiological study – This test is used to determine the exact location where an irregular heartbeat starts. It involves specific flexible tubes that are inserted into a blood vessel and then guided to the heart.
Treatment
While most people with this condition do not need treatment, some of them experience irregular heartbeats for long periods and may need it. Check below the most common treatments recommended for people with atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia:
- Vagal maneuvers – There are some actions (such as coughing, bearing down as if passing stool, massaging the main artery in the neck, or putting an ice pack on the face) that may help control heartbeats.
- Medications – Healthcare professionals may recommend some medications if you experience fast heartbeats.
- Cardioversion – This treatment uses specific paddles or patches that are attached to the chest to deliver small electrical shocks to the heart. It helps restore normal heart rhythm. It is often recommended by doctors when vagal maneuvers and medications are not effective.
- Catheter ablation – Doctors usually prescribe this treatment for people with severe adverse reactions or when medicines do not work. It involves a small and flexible tube (also known as a catheter) that is inserted into a major blood vessel, often in the groin, and then guided to the heart. Therefore, the catheter uses heat or cold energy to make small scars in the heart. As a result, it blocks irregular electrical signals and helps restore typical heartbeats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What can cause atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia?
These include:
- Heart diseases (such as heart valve disease, coronary artery disease, and others)
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Congenital heart defects (heart conditions present at birth)
- Lung disease, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Thyroid disease
- Recent heart, lung, or throat surgery
- Heart failure
If you suspect you have AVNRT, do not hesitate to see a doctor.
Can AV nodal reentry tachycardia be cured?
The only treatment that can cure some types of arrhythmia is catheter ablation. It is used to make small scars in the heart that block abnormal electrical signals. For more details, discuss it with your doctor.
How rare is AVNRT?
In general, atrioventricular nodal reentry tachycardia is considered a sporadic disease that happens in 22.5 cases per 10,000 in the population. However, most people with this condition do not need treatment. Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.