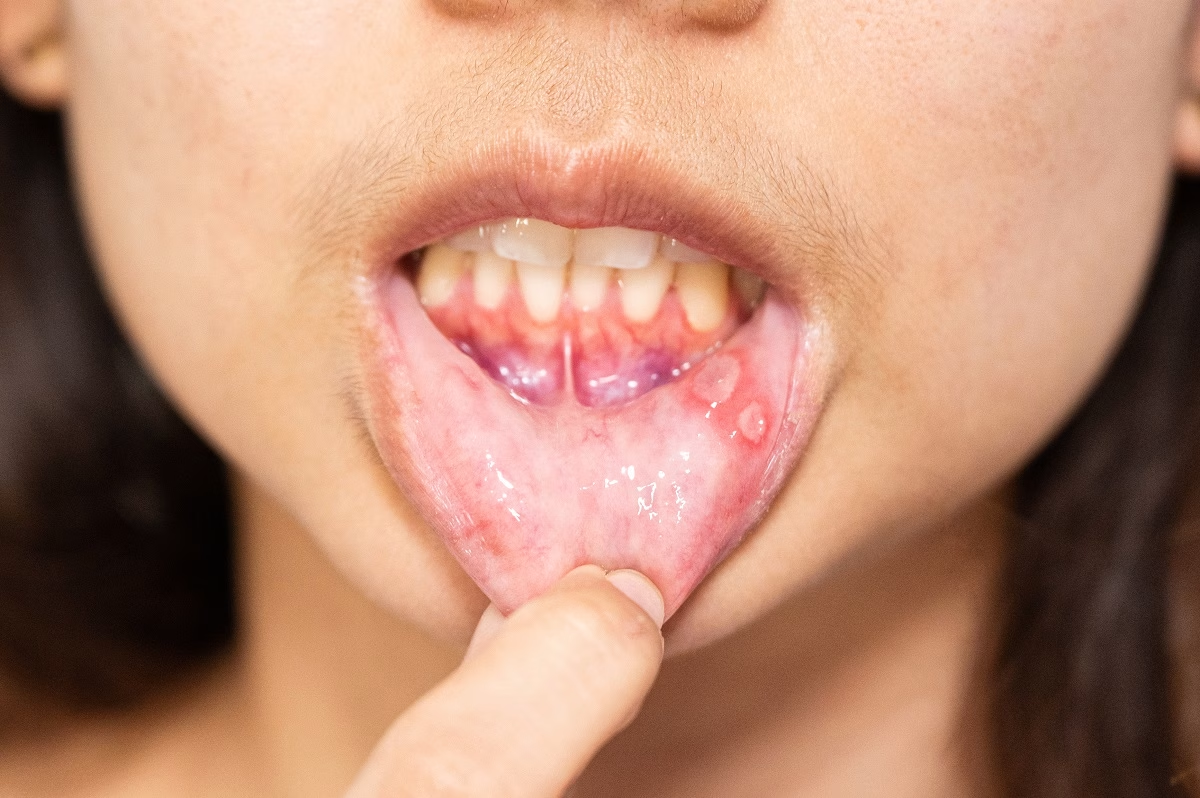
A condition in which the lining of the mouth and lips becomes inflamed is called stomatitis (also known as oral mucositis). In most cases, people develop the following types of this disorder. For example, cold sores and canker sores. This disorder may occur due to multiple reasons, including allergic reactions, adverse reactions to cancer treatments, infections, injuries, and others. Commonly, treating the underlying condition helps get rid of stomatitis. During treatment, doctors may also recommend some medicines to reduce the symptoms.
Furthermore, this condition may also affect the mucous membranes that line the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Inflammation often occurs as a natural body response to injury or something that causes damage to the mucosa in the mouth. While in most cases, they are not serious and go away on their own, some people may need prescription medicines to treat the condition.
Types of Stomatitis
The most common types of this disorder include canker sores and cold sores. The first appears inside the mouth, and the second type causes fluid-filled blisters that may appear alone or in clusters around the mouth. Check below for other types of stomatitis that occur less commonly:
- Angular cheilitis (also called angular stomatitis) – This type causes irritation, sores, and cracks in the corners of the mouth.
- Thrush (candidal stomatitis) – In such cases, the condition causes an overgrowth of Candida fungi in the mouth.
- Contact stomatitis – It often causes inflammation in the mouth due to an allergic reaction.
- Denture stomatitis – This type often affects people who wear dentures. It causes irritation in the mouth along with candidal stomatitis.
- Gingivostomatitis – People who develop this type of stomatitis experience inflammation of the mouth or gums due to a viral or bacterial infection.
- Nicotine stomatitis – It often affects people who smoke or use tobacco. The most common symptoms include white or cobblestone-like patches of tissue in the roof of the mouth.
Symptoms
Usually, people who develop stomatitis may experience the following symptoms. Examples include:
- Swelling and redness inside the mouth
- A small blister or cluster of blisters around the lips
- One or multiple sores inside the mouth. These sores are often white, gray, or yellow with a red border.
- Gray or white patches on the tongue, cheeks, or roof of the mouth
- A feeling like your tongue or the roof of your mouth is burning
- Discomfort or pain that makes it difficult to talk and swallow
IF any of the previous symptoms occur, do not hesitate to see a doctor, especially if they do not go away within a few days.
Causes
This condition may occur due to multiple reasons. These include immune system disorders, mouth injuries, viral infections, and others.
- Infections – One of the most common causes of stomatitis is an infectious disease caused by HSV-1 (the herpes virus). However, it may also occur due to bacterial and fungal infections.
- Mouth injuries – Anything that causes damage to the mucous membrane inside the mouth may trigger the body’s healing response, which often causes inflammation. It may include ill-fitting dentures, smoking cigarettes, and other factors.
- Allergic reactions – There are some substances that may irritate the mouth. For example, dental products (such as mouthwash), cosmetics (including lipstick), or spicy foods.
- Certain treatments – For example, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and other cancer treatments. Almost everyone who gets these treatments develops stomatitis.
- Medicines – The following medications are often associated with stomatitis. Examples include immunosuppressants, beta-blockers, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Systemic disorder – there are some disorders that affect multiple body systems. As a result, it may lead to stomatitis. For example, Behcet’s disease, Celiac disease, skin disorders (including bullous pemphigoid and lichen planus), and others.
- Nutritional deficiencies – People who do not get enough nutrients from their diet may experience stomatitis. In most cases, it involves deficiencies in folate, iron, vitamins B12 and C, and zinc.
Risk Factors
While this condition can affect anyone, some people are at increased risk of developing it. Check below some examples:
- Poor dental hygiene
- Dry mouth
- Denture use
- Medicines (such as antibiotics)
- Infections
- Cancer treatments
- Hormonal imbalances
- Smoking
- Genetic factors
This article does not contain all possible factors that could increase your risk of developing stomatitis. For more details, discuss it with your doctor.
What Are The Possible Complications of Stomatitis?
In some cases, people with stomatitis may also experience some complications. These include:
- Dehydration
- Malnutrition
- Secondary infections
- Herpes simplex encephalitis (brain inflammation)
- Gangrenous stomatitis
- Scarring
You can talk with your doctor about ways to prevent previous complications.
How to Prevent Stomatitis?
Generally, it is not possible to prevent all causes of stomatitis. However, the following tips may help reduce the risk. For example:
- Adopt a healthy diet and drink plenty of water
- Brush and floss twice a day and get regular dental cleanings
- Quit smoking (if you face problems with smoking cessation, it is recommended to discuss it with your healthcare professional)
- Do not share your foods, drinks, or personal items (such as lipstick), especially with a person with canker sores
Diagnosis
Physicians usually begin the diagnosis with a physical examination to check for abnormalities linked to the disease. They may also ask some questions about the symptoms and review your medical history. However, in some cases, doctors perform the following tests to confirm the condition and rule out other conditions that cause similar symptoms. Check below some examples:
- Tests to check for bacteria, viruses, or fungi
- Blood tests to check general health and get more clues about the disease (such as signs of systemic disease)
- Allergic tests
- Biopsy – during this procedure, doctors will take a small sample of the affected tissue to test it under a microscope. It helps identify a more serious disease.
Treatment
Physicians usually recommend different treatments for people with stomatitis. IT depends on the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, age, existing health problems, and preferences. Check below the most common treatments recommended for people with stomatitis:
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers and other medicines to treat canker and cold sores
- Antivirals, antibiotics, and antifungals to treat infections
- Supplements and vitamins to prevent deficiencies
- Your doctor may also recommend good oral hygiene to make sure your mouth is free of harmful bacteria
Moreover, healthcare professionals may also recommend some medicines along with previous treatments to ease pain and inflammation. For example, corticosteroids, topical anesthetics, and magic mouthwash.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should I see my healthcare provider?
If you experience any of the following symptoms, immediately contact your doctor. These include:
- High fever (more than 100.4 °F or 38 °C)
- Rash or blisters on the skin
- Eye pain, redness, or swelling
- Vision changes (such as blurred vision)
Does stomatitis go away on its own?
Most of the time, this disorder goes away on its own. However, your doctor may recommend some OTC medicines to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. For more details, discuss it with your doctor.
Can stomatitis be cured?
In some cases, this condition can be cured. It depends on the underlying cause. For instance, herpetic stomatitis cannot be cured because the virus remains in the body, but outbreaks can be treated with medicines. Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.