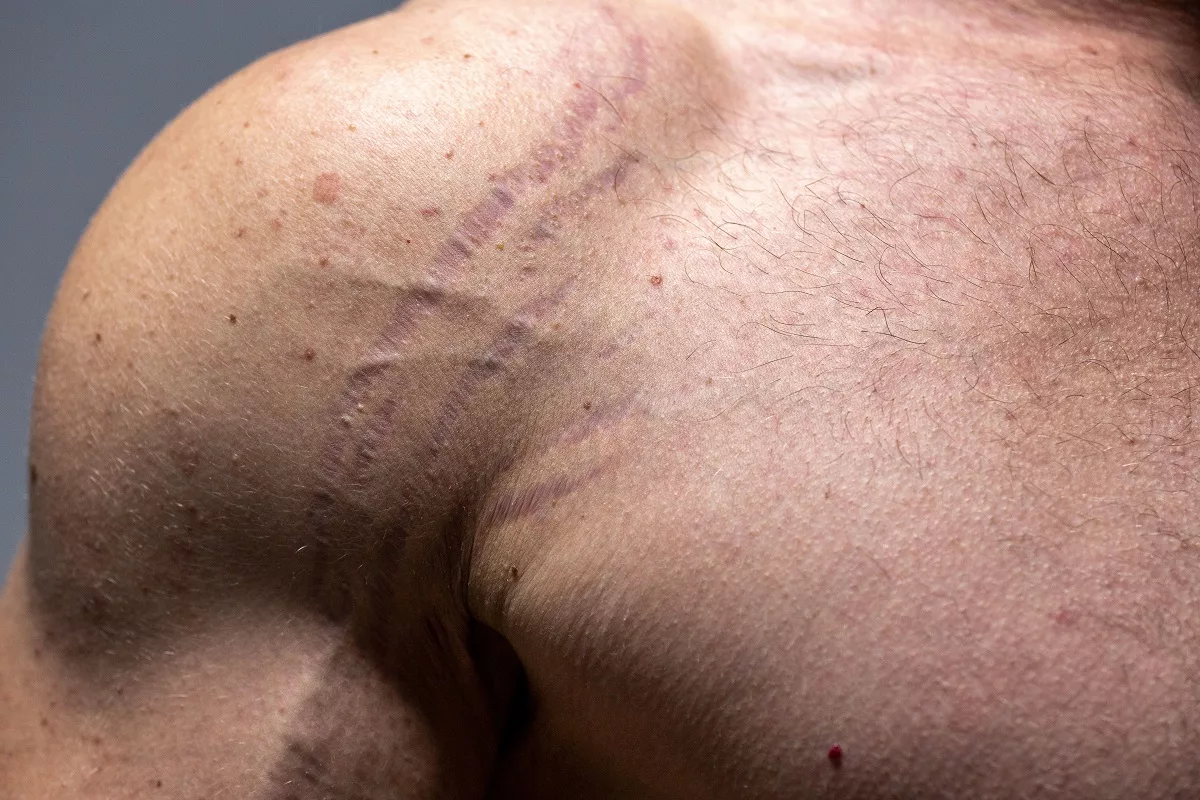
The tissue that the body builds to repair damaged skin due to an injury is called a scar. Generally, this is a part of the body’s healing process. The scars appear in different sizes and shapes depending on their cause. For example, accidents, burns, surgery, acne, or other health conditions. While most scars fade away over time, some of them do not disappear without treatment.
The scars are made mainly of a protein known as collagen. Furthermore, some people may develop large scars that cause pain. However, people with darker skin (including people with African, Asian, or Hispanic heritage) are more likely to develop a specific type of scar called keloid scars. This type causes raised scars to grow that sometimes may extend over the injured area.
In general, scars are common. Almost everyone develops a certain type of scar from a surgical procedure, accident, acne, or disease (such as chickenpox, also known as varicella)
Types
Healthcare professionals have divided this condition into several types, based on the exact cause of the scars. Check below some examples:
- Contracture – This type often appears after a burn. It causes the skin to tighten (contract). In some cases, contracture scars can make it difficult to move, especially when scarring occurs in the muscles or nerves.
- Depressed (also known as atrophic) – In such cases, scar tissue appears due to certain health conditions, such as acne or chickenpox. Usually, they look like rounded pits or small indentations in the skin. Sometimes, this type of scar is called ice pick scars.
- Flat – These scars are usually pink or red and become flat when they heal.
- Keloids – This type of scar often appears above the skin’s surface and may spread over the affected area.
- Hypertrophic (raised) – People usually feel this type of scar when they run their finger over it. While it never flattens completely, it does not grow over the affected area.
- Stretch marks – People usually develop this type of scar when the skin expands or shrinks too quickly. When it occurs, the tissue under the skin is damaged. In most cases, stretch marks appear during pregnancy, puberty, or after gaining or losing weight. In most cases, this type of scar appears on the breasts, stomach, thighs, and upper arms.
In some cases, people may develop a type of scar that makes the tissue build up inside the body. These scars are called internal scar tissue, and they may occur due to surgery (such as abdominal adhesions), health conditions (such as Asherman’s syndrome and Peyronie’s disease), and certain autoimmune disorders (such as scleroderma).
Symptoms
Scars usually appear pink or red, especially on lighter skin, and over time may become lighter or darker than the skin color. Those who have darker skin, scars may appear as dark spots and sometimes cause itching and pain. Check below some factors that affect the shape and form of a scar:
- An injury or event that causes a scar, including a car accident, surgery, burn, or severe acne
- The severity and exact location of the wound
- Treatments to heal the wound (including bandages, stitches, and others)
- Your overall health, age, genes, and ethnicity
Causes
The skin is a protective barrier that helps prevent the entry of germs and other harmful substances into the body. When the skin is damaged, the body begins to make new tissue to reseal itself. This tissue is made of collagen. Furthermore, collagen plays multiple important roles in the body, including pumping up the skin, protecting cartilage and joints, and others.
What Are The Potential Complications of Scars?
Sometimes, people may experience some complications. It depends on the type and cause of scar, existing health problems, and other factors. Check below some examples:
- Itching
- Pain and tenderness
- Physical deformity (usually due to hypertrophic or keloid scars)
- Increased risk of skin cancer
- Psychological distress (including depression, post-traumatic stress, anxiety, and others)
This document does not contain a full list of scar complications. However, you can consult with your healthcare professional to reduce the risk or even prevent these complications.
How to Prevent Scars?
Usually, it is not possible to prevent injuries that cause scars. However, you can take certain steps to reduce the risk of scar formation after an injury. Check below some tips:
- Visit a healthcare professional – If you develop a scar that causes discomfort, it is recommended to see a doctor. Some people may need stitches or bandages to hold the skin while it heals. Moreover, stitches may reduce scarring.
- Clean the wound – It is recommended to clean the wound with soap and warm water to remove dirt or dried blood. Thereafter, you should apply a bandage over the affected area to prevent the entry of germs.
- Maintain the wound moist – You should not let the wound to become dry because it increases the risk of developing a scab. Usually, scabs worsen scarring.
- Get protection against UV rays – Regularly cover the affected area to protect against the sun, especially when outdoors. Prolonged exposure of the wound to the sun significantly increases the risk of skin cancer.
- Supplements – You should consult with your doctor about vitamins required to maintain high-quality protein levels in the body. These proteins are required for healing.
Diagnosis
Usually, doctors diagnose this condition during a physical examination. They may also evaluate a scar that is causing problems (such as pain). To determine the type of scar, doctors will look at the size, texture, and color of the scar.
Treatment
Physicians recommend different treatments for those who develop scars. It depends on the type, size, and location of the scar. Check below some treatment options:
Dermabrasion
This is one of the most common treatments recommended for people with acne scars. It also helps soften and smooth the skin and improve the appearance of scars.
Injections
Sometimes, you may get a prescription for Corticosteroid injections. They are often used on people with keloid scars. Moreover, physicians may inject certain drugs to treat cancer (including Bleomycin and Fluorouracil) to flatten scars and lessen symptoms (such as itching and pain).
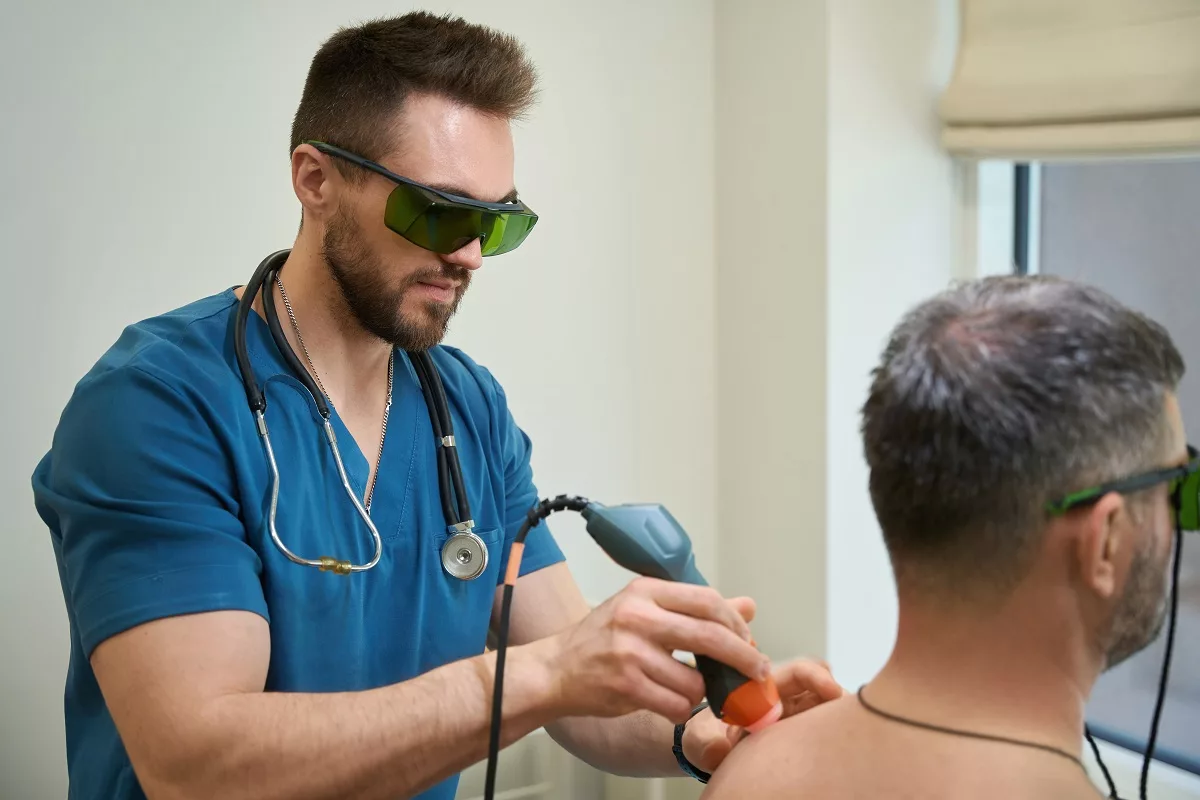
Laser Therapy
In general, there are several types of laser and light treatments used to treat acne scars. However, laser options use a wavelength of light to perform specific actions in the skin. For example, the V beam is a pulsed dye laser that targets small blood vessels in the skin. In some cases, after this treatment, the scars may remain red or pink because of new blood vessels that have developed to heal the affected area. While laser treatments help to make the scars less noticeable, they can cause hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation, especially in people with darker skin.
Pressure Therapy
This treatment involves bandages, dressings, or stockings that put pressure on the affected area to improve the healing process. Doctors may also recommend massage therapy to break up the tissue and allow it to remodel.
Scar-revision Surgery
There are several types of surgery that can be used to improve the appearance of a scar. In some cases, doctors may transplant the skin from another area (also known as a skin graft).
Topical Ointments and Creams
People who use silicone ointment right after injury may develop a smaller scar or even prevent it. In some cases, doctors may prescribe Corticosteroid creams.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main types of scars?
The primary types include atrophic, hypertrophic, and keloid. Thus, the atrophic scars are indented or sunken, hypertrophic scars are often raised and confined to the affected area, and keloid scars raise beyond the wound area.
Does Vaseline help scars?
Yes, this medicine can be used to improve the appearance of scars. It also helps maintain the affected area moist, which prevents scabs. However, consult with your doctor before using Vaseline.
Which scars are permanent?
While there are multiple types of scars, keloid and hypertrophic scars are often permanent. Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.