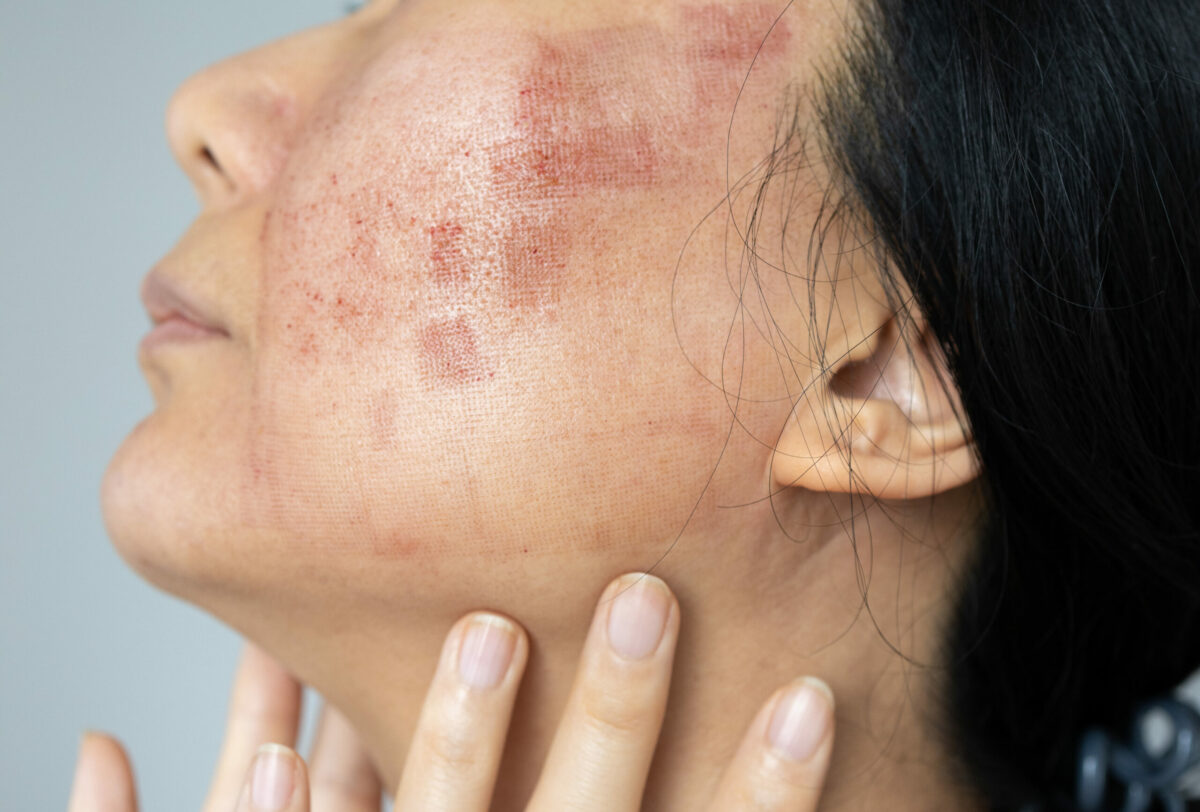
Health conditions that provoke inflammation of the skin are called dermatitis. For example atopic dermatitis (eczema), contact dermatitis, and seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff). These skin conditions usually provoke different symptoms. For example dry skin, red rashes, itchiness, and others. Commonly, healthcare professionals or dermatologists help to treat dermatitis.
What is Dermatitis?
The word “dermatitis” means all skin irritations and rashes caused by different health conditions. For example genetic diseases, an overactive body’s defense (immune system), infections, allergies, irritating substances, etc. The most common symptoms are red, dry, and itchy skin. The rashes can be mild to severe and provoke different problems. In most cases, dermatitis does not cause any serious problems to the body and it is not contagious. Unfortunately, dermatitis cannot be cured but suitable treatment can lessen the symptoms.
Dermatitis Types
- Stasis dermatitis
- Seborrheic dermatitis (cradle cap, dandruff)
- Periorifical or perioral dermatitis
- Nummular dermatitis
- Neurodermatitis
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis
- Diaper dermatitis (rash)
- Contact dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema)
Risk Factors
Anyone can develop dermatitis whether you are young or old. Check below some risk factors:
- Atopic dermatitis (females, African American people, family history of dermatitis, hay fever, or asthma)
- Contact dermatitis (if you are working with or around chemicals including a factory, restaurant, or garden)
- Periorifical dermatitis (females, especially between 15 to 45 ages)
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis (excessive sweating, living in a warmer climate, and exposure to irritants or water for long periods)
Usually, the type of dermatitis depends on where it appears. Examples include atopic dermatitis (anywhere on the skin but in adults on the hands, inner elbows, neck, knees, ankles, and feet), seborrheic dermatitis (usually on the scalp, face, and ears), periorificial dermatitis (often appears around eyes, mouth, nostrils, and rarely genitals). Fortunately, dermatitis is not a contagious condition. In some cases, people with dermatitis may experience pain or burning sensations. However, the sensations are different among people. The first dermatitis symptoms usually are itchiness and redness.
Is There a Difference Between Dermatitis and Psoriasis?
These skin conditions can look very similar (especially seborrheic dermatitis). Red skin with flakes of skin on top and around the redness are symptoms that can occur in both conditions. The only difference is that the scales are usually thicker and well-defined in psoriasis. Furthermore, psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis may combine into a health condition called “sebopsoriasis”. Thus, people will experience symptoms of both diseases. If you experience one or two dermatitis at the same time, it is advised to visit a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
What is The Difference Between Rosacea and Dermatitis?
One symptom of rosacea is red skin, which looks very similar to one of the dermatitis symptoms. In any case, rosacea also provoke pimples and redness is located on the forehead, nose, chin, and cheeks. See a doctor to determine which type of skin condition you have such as dermatitis, rosacea, psoriasis, or others.
Symptoms
Usually, the symptoms vary among people because it depends on the severity and type you have. For example:
- Itching
- Red rashes
- Bumps
- Rashes that look such as burns
- Dry skin
- Fluid-filled blisters
- Swelling, thickening, and hardening of the skin
- Painful ulcers
- Creasing, scaling, and crusting skin
- Oozing, bleeding, or fluid when the skin is scratched
In addition, check below symptoms of the most common dermatitis types:
- Atopic dermatitis (eczema) – Skin inflammation, redness, itchiness, dryness, and bumpy
- Contact dermatitis – Painful and itchy skin rash
- Seborrheic dermatitis (cradle cap) – Usually, occurs in children and appears as yellow scaly patches with a red rash
- Diaper dermatitis (rash) – This condition happens in babies and the skin gets broken.
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis – This skin disease type provokes itchy blisters on the edges of the palms, fingers, toes, and soles of the feet.
- Neurodermatitis – Intense itching that causes irritation of the nerve endings on the skin.
- Nummular dermatitis – The skin becomes dry and itchy and sometimes you may get open sores.
- Periorificial dermatitis – This skin condition type looks similar to acne and rosacea because it often develops around the mouth, nose, and eyes.
- Seborrheic dermatitis – Appears as dry, flaky, red, itchy skin usually on the scalp. However, it may occur in other parts of the body.
- Stasis dermatitis – This skin disease is commonly caused by a blood flow problem that provokes ankles to swell. This effect can lead to scaling, itching, pain, and open sores.
Does Stress Cause Dermatitis?
Many skin conditions including dermatitis can occur due to stress. Check below some mental and emotional symptoms of stress:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Depression
- Low self-esteem
- Cannot relax and using alcohol, tobacco, or street drugs to relax
- Irritability, mood swings, a short temper
- Constant anxiety and worry
- Feeling overwhelmed
Check below some physical stress symptoms:
- Muscle tension, aches, or pains
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Sleeping more or less
- Feeling nauseated or dizzy
However, you can follow the next steps to reduce the stress:
- Journal
- Limit alcohol and caffeine drinks
- Eat healthy meals
- Regular exercise
- Try to have a positive attitude
- Get enough sleep
- It is advised to accept that you cannot control everything
- Take deep breaths
- You can also consult with a therapist or talk with friends or family
What Triggers and Worsens Dermatitis?
There are different factors that can trigger or worsen a dermatitis. However, it is important to figure out what triggers your dermatitis because you can control it. For example, you should pay attention to the chemicals that you are using, if you are around smokers, new shampoo that provokes itching, new perfumes, and excessive sunlight may also trigger dermatitis. However, the following factors can worsen the dermatitis. For example:
- Allergens (including pollen)
- Pet dander
- Hot showers
- Stress
Treatment
Commonly, the treatment method depends on the dermatitis type and its location. The second step in dermatitis treatment is to determine what triggers the condition. Thereafter, your doctor may prescribe some medications that will help to lessen the symptoms and treat the condition. Check below some examples of medications:
- Moisturizing creams (hydrate and restore skin)
- Calcineurin inhibitors (reduce inflammation)
- Corticosteroid creams and ointments
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors
- Biologics (injections that block the immune system function)
- Oral medicines
- Antihistamines
- Antibiotics (usually used in the treatment of perioral dermatitis)
Additionally, there are some tips that you can do at home without supervision. Examples include:
- Do not overheat
- Use moisturizers
- Protect your skin
- Manage stress
- Bathe in lukewarm water
- Avoid scratching
- Use a mild soap
Consult with your doctor for more details.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can dermatitis damage the skin permanently?
In case you scratch the skin too much, scars may appear.
What foods should I avoid to decrease the risk of dermatitis?
For example, eggs, dairy, peanuts, sugar, and alcohol are foods that could provoke dermatitis.
What are the possible complications of dermatitis?
Not treating this condition may lead to some unpleasant complications. Examples include:
- Viral skin infections
- Bacterial skin infections
- Sleep loss
- Conjunctivitis (pink eye)
- Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid)
If you experience any of the complications listed above, talk with your healthcare professional.