There are two types of brain tumors including benign or noncancerous and malignant or cancerous. This condition can be experienced by anyone from children to adults. It usually does not matter what type of tumor a person has either malignant or benign, it may lead to some brain function problems. This happens because these tumors grow enough to put pressure on the nearby tissues. However, several treatment options are available to reduce the symptoms and improve your quality of life.
What is Brain Cancer?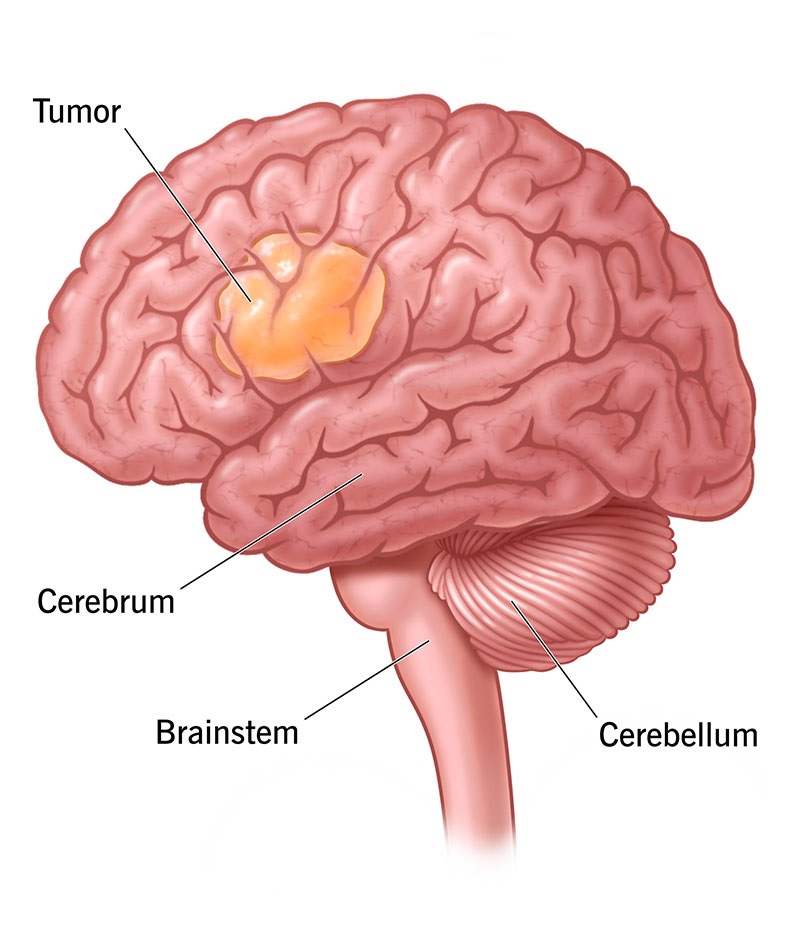
An abnormal growth of cells in or around the brain is a brain tumor that can be cancerous or noncancerous. While some of them grow quickly, others are slow. Additionally, spinal tumors and brain tumors together are usually called central nervous system (CNS) tumors. Approximately 33% of all brain tumors are malignant.
There are tumors that develop in the brain are known as primary tumors but those that spread to the brain from other different parts of the body are called metastatic brain tumors or secondary tumors.
Brain Tumor Types
There are more than 150 brain tumors. Experts classify primary tumors as being glial (created from glial cells in the brain), non-glial (that are produced in certain brain structures including nerves, glands, and blood vessels), and malignant (cancerous) or benign (noncancerous). Moreover, many brain tumors can develop in the spinal cord or column.
Common Benign Brain Tumors
- Chordomas – These are slow-growing tumors that usually start at the base of the skull and bottom part of the spine.
- Craniopharyngiomas – These tumors usually spread from the pituitary gland and are quite difficult to remove because they are near important brain structures.
- Gangliocytomas, gangliomas, and anaplastic gangliogliomas – They form usually in neurons (nerve cells) but are very rare tumors.
- Glomus jugulare – Mostly, they develop under the skull base at the top of the jugular vein (also known as the neck vein). Furthermore, it is considered one of the most common glomus tumors.
- Meningiomas – These tumors are the most common primary brain tumor type. Commonly this tumor grows slowly and forms in the meninges (certain tissues that protect the brain and spinal cord).
- Pineocytomas – These are also slow-growing tumors that happen in the pineal gland. This is a gland that releases the melatonin hormone and it is located deep in the brain.
- Pituitary adenomas – These are pituitary gland tumors. This gland is responsible for producing and controlling hormones in the body. Usually, these adenomas cause an increased release of pituitary hormones.
- Schwannomas – They are considered the most common noncancerous tumors in adults. This type usually develops in the peripheral nervous system or cranial nerves in Schwann cells. The most common schwannoma is considered acoustic neuroma. The tumor develops in the vestibular nerve which leads from the inner ear to the brain.
Cancerous Brain Tumors
About 78% of malignant primary brain tumors are gliomas and they form in glial cells that assist and surround nerve cells. Check below some examples:
- Astrocytoma – These are the most common glioma type and happen in the star-shaped glial cells (astrocytes). This glioma type also can occur in different brain parts but mostly in the cerebrum.
- Ependymomas – They occur near the brain’s ventricles.
- Glioblastoma (GMB) – These are fast-growing astrocytomas because they develop in glial cells (astrocytes).
- Oligodendroglioma – This type occurs rarely and starts in certain cells that produce myelin. This is a layer of insulation near nerves in the brain).
Another malignant form of brain tumor is medulloblastoma. They usually happen in children and are fast-growing tumors that appear at the skull base.
Who’s Impacted by Brain Tumors?
These tumors are a little bit more common in men and people assigned to male at birth (AMAB) than women and people assigned to female at birth (AFAB). The only brain tumor type that is more common in AFAB is meningioma. Glioblastoma is considered the most severe type of brain tumor.
Are Brain Tumor Serious Condition?
It is not necessary to only malignant tumors provoke problems however, benign also cause brain function issues. It happens because the growing tumor puts pressure on certain tissues near the brain. Check below some symptoms:
- Partially or completely vision loss
- Memory problems
- Difficulty understanding
- Balance issues
- Walking problems
- Weakness
Check below some problems that brain tumors can cause:
- Put pressure on nearby brain tissues
- Destroy healthy tissue in the brain
- Intracranial pressure
- Provoke fluid to build up in the brain
- Bleeding in the brain
- Disrupt the usual cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) flow
In any case, some people with brain tumors do not experience any symptoms because the tumor does not grow. As a result, it does not put any pressure on nearby brain tissues, blood vessels, and others.
Symptoms
In most cases, people with brain tumors do not have any symptoms, especially if the tumor is small. However, the symptoms usually depend on the tumor’s location and size. Check below some examples:
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Thinking or speaking problems
- Personality changes
- Weakness
- Paralysis
- Balance issues
- Dizziness
- Vision changes
- Hearing problems
- Facial numbness or tingling
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Confusion
- Disorientation
In case you experience any of the symptoms listed above, it is advised to visit a doctor right away.
Causes
Experts know that tumors that develop in the brain are provoked by the damaged genes on the chromosomes and are not working properly. However, they do not understand why it happens. The DNA located in the chromosomes tells cells in the body when to divide, multiply, grow, or die.
Once a change occurs in brain cell DNA, appear new instructions. As a result, abnormal brain cells begin growth and multiply quicker than usual. Over time, these abnormal cells take up more space in the brain.
Rarely, someone can be born with one or more damaged genes. In addition, further damage can also cause the following environmental factors including exposure to radiation usually from X-rays or other cancer treatments. Check below some examples of inherited genetic syndromes that could contribute to or cause brain tumors:
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 and type 2 (NF1 and NF2 genes)
- Turcot syndrome (APC gene)
- Gorlin syndrome (PTCH gene)
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome (TH53 gene)
- Tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC1 and TSC2 genes)
Those who experience brain tumors due to genetic factors have a family history and account for 5%-10% of cases.
Diagnosis
A brain tumor diagnosis is commonly difficult and includes more healthcare specialists. However, physicians may notice a brain tumor while doing imaging tests for another disease. Healthcare professionals will perform a physical examination if you experience any brain tumor symptoms. They also will ask some questions about your symptoms, existing health conditions and treatments, surgeries, and family history.
In any case, if doctors are not sure whether you have a brain tumor or not, they can perform a neurological examination that includes testing for changes in your:
- Mental status
- Vision and hearing
- Reflexes
- Balance and coordination
If your healthcare professional suspects you have a brain tumor, the next step is a brain scan (MRI). Check below some examples of tests involved in brain tumor diagnosis:
- Brain MRI or CT scan – Before these scans, your doctor will administer a contrast agent in the vein because this substance can help to identify a tumor more easily. However, MRI and CT scans can be used to check different parts of the body (including lungs, colon, breasts, and others).
- Biopsy – This test involves the removal of a small piece of tumor for a microscope examination.
- Spinal tap – During this procedure, your doctor will remove cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) using a needle.
- Specialized tests – Blood and cerebrospinal fluid tests are done to check for tumor markers. These markers are released by the tumors.
Treatment
The treatment often depends on your tumor’s location, size, type, age, and overall health. In most cases, benign tumors are successfully removed by surgery and they are not growing back usually. Physicians prescribe commonly a combination of therapies to treat a tumor. Check some examples below:
- Brain surgery (craniotomy)
- Radiation therapy
- Radiosurgery – This treatment method involves focused beams of radiation (gamma rays or proton beams) to destroy the tumor.
- Brachytherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
Check below some additional tests used to relieve the symptoms:
- Shunts
- Medicines (including Mannitol and Corticosteroids)
- Palliative care
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to prevent brain tumors?
It is impossible to prevent a brain tumor but you can reduce the risk of its development. For example, quit smoking and reduce exposure to radiation. Consult with your doctor for more details.
What are the 10 symptoms of a brain tumor?
It is advised to see a doctor if any of the following symptoms occur. Examples include:
- Difficulty concentrating
- Sluggishness
- Weakness
- Speaking problems
- Loss of smell
- Aggression or agitation
- Reduced impulse control
- Personality, mood, or behavior changes
Is it hard to sleep with a brain tumor?
Sleep disturbances (insomnia) are considered a common symptom of a spine or brain tumor. Ask your healthcare professional if you have any additional questions.