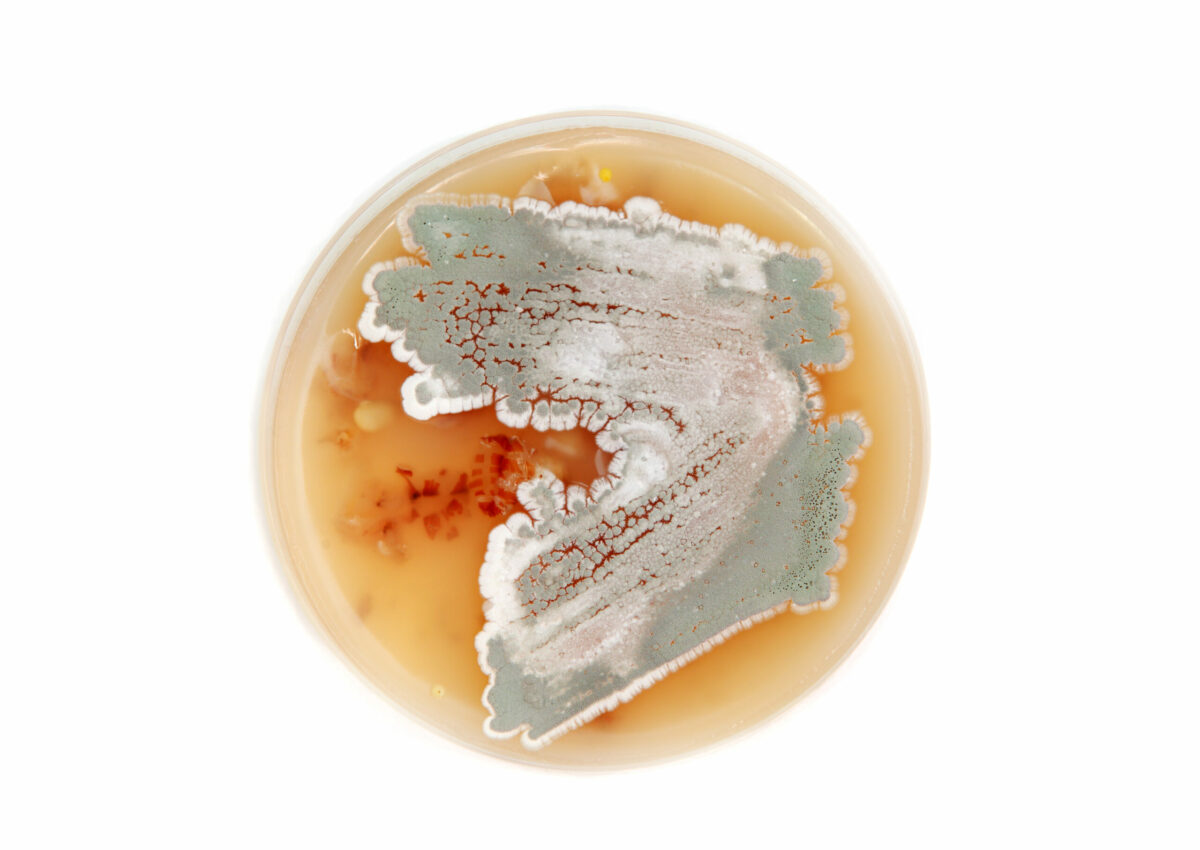
A fungal infection that happens due to coccidiosis organisms is called valley fever. The most common symptoms include cough, fever, and tiredness. However, there are two fungi types that cause valley fever. These species are found in soil in multiple regions. Moreover, spores of these fungi may be stirred into the air by roughly anything that touches infected soil including farming, construction, and wind.
Humans usually get the fungi when breathe and it goes to the lungs. These fungi can cause valley fever also called acute coccidiodomycosis. While mild forms of this condition go away without treatment, more severe types require antifungal medications.
Symptoms
The initial form of the coccidiodomycosis infection is called valley fever. However, this infection may develop into one more serious including chronic and disseminated coccidiodomycosis.
Acute Coccidiodomycosis also known as Valley Fever
This initial or acute form of the infection is commonly mild with little or no symptoms at all. Moreover, they usually appear within 2-3 weeks after exposure to the fungi and may be similar to the flu symptoms. Check below some examples:
- Fever
- Shortness of breath
- Tiredness
- Chills
- Night sweats
- Joint aches
- Muscle soreness
- Red rash on the lower legs and sometimes on the chest, arms, and back
- Cough
- Headaches
Sometimes, people do not experience any symptoms and find that they were been infected later by performing blood tests or a routine X-ray. Those who develop severe symptoms usually need months to recover and some symptoms may last even longer. There are several factors that determine how severe the condition is such as the amount of fungus you inhale, existing health problems, and others.
Chronic Coccidioidomycosis
People who do not treat the acute form of the infection completely may develop this type. It often happens in people with weakened immune systems. Check below some symptoms:
- Low-grade fever
- Cough
- Chest pain (angina)
- Weight loss
- Blood-tinged sputum
- Nodules that happen in the lungs
Disseminated Coccidioidomycosis
This type of infection is the most severe and happens quite rarely. Commonly, people experience disseminated coccidioidomycosis when the fungi spread from the lungs or other body parts. These include the skin, bones, liver, brain, heart, meninges (protective membranes) of the brain and spinal cord, and others. Check below some symptoms:
- Swollen and painful joints in the ankles or knees
- Painful lesions in the skull, spine, or other bones
- Ulcers, skin lesions, and nodules
- Meningitis (a condition in which the membranes that protect the brain and spinal cord become infected)
Immediately seek medical care if you are pregnant, are over 60 years old, or weakened immune system and experience valley fever symptoms.
Causes
This condition often happens when a person inhales spores of specific fungi including Coccidiodes immitis or Coccidiodes posadasii. These fungi live in the soil of Arizona, Nevada, Utah, New Mexico, California, Texas, and Washington. Moreover, these fungi types also can be found in northern Mexico and Central and South America.
Species of coccidiodes are similar to other fungi types and have a complex life cycle. For instance, they appear in the soil as a mold with long filaments that may break into airborne spores when the soil is disturbed or these spores can be carried by wind. Infection occurs when a person inhales these fungi spores and they get into the lungs. Once they enter the lungs, spores begin to multiply and cause the disease.
Risk Factors
There are some factors that may elevate your risk of developing valley fever. Check some of them below:
- Environment factors – The risk of developing valley fever increases in anyone who inhales the fungi spores. People who live in regions where this fungi type is common are at higher risk of developing this infection. In addition, those who work in construction, road and agricultural workers, ranchers, archeologists, and military personnel are more prone to develop this infection.
- Race – Experts do not fully understand why people of Filipino and African heritage are more likely to develop this disease.
- Pregnancy – Pregnant women are more prone to develop the infection, especially during the third trimester.
- Weakened immune system – People with weakened immunity are at higher risk of developing this infection. In most cases, the immune system becomes weakened due to HIV/AIDS, certain medications (such as steroids and chemotherapy), autoimmune conditions (such as Crohn’s disease or rheumatoid arthritis), and others.
- Diabetes – Those who experience diabetes also are at increased risk of developing valley fever.
- Age – The immune system becomes weakened in older people as a normal part of aging. Therefore, the risk of developing valley fever increases significantly.
Complications
People who have HIV infection, with a weakened immune system, and pregnant women are at higher risk of developing the more severe type of coccidioidomycosis. Check below some complications:
- Severe pneumonia – While most people recover from coccidioidomycosis-related pneumonia, some people may develop serious or even life-threatening conditions.
- Lung nodules – Sometimes, nodules may break and cause chest pain and breathing problems.
- Disseminated disease – This complication is the most severe form of the infection and it happens when the infection goes from the lungs to other body parts. Therefore, it may cause skin ulcers, abscesses, bone lesions, severe joint pain, inflammation of the heart, urinary tract problems, meningitis, and others.
How to Prevent Valley Fever?
Unfortunately, there is no way (such as a vaccine) available to prevent this condition. However, the following tips may help reduce the risk of infection. Examples include:
- Weak a mask
- Do not stay in very dusty areas (such as construction sites)
- Do not outdoors during dust storms
- It is advised to wet the soil before digging or even avoid it if you are at increased risk of developing the infection.
- You should keep windows and doors closed
- Skin injuries should be washed thoroughly with soap and warm water
Diagnosis
First, doctors will evaluate your medical history and ask some questions about your symptoms. However, it is quite difficult to diagnose this condition based only on the symptoms because there are other diseases that cause similar ones. Furthermore, an X-ray test cannot help doctors determine the difference between valley fever and other lung conditions (such as pneumonia). That’s why physicians perform the following tests. For example:
- Sputum smear or culture – This test involves a sample of the sputum discharged while coughing for the presence of coccidiosis.
- Blood tests – These tests are done to check for antibody levels that are present in people with valley fever.
Treatment
The treatment for valley fever includes supportive care and in more severe cases medications. However, people with mild forms of valley fever do not require treatment. Anyway, they are monitored carefully by doctors.
Antifungal Medications
People who do not notice any improvements, experience the infection for a prolonged time, or are at increased risk of complications usually get antifungal medications. Physicians often recommend Fluconazole or Itraconazole. On the other hand, all antifungal medicines may give you severe adverse reactions. These include nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, diarrhea, hair loss, dry skin and mouth, and others.
For people with disseminated coccidioidomycosis, doctors prescribe Amphotericin B, Voriconazole, Posaconazole, or Isavuconazonium sulfate.
In addition, some people develop lifelong immunity to this infection after the first time they get infected. The only way the infection may return is a weakened immune system.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a human get Valley fever?
People often get infected with this fungi when inhaling its spores. This fungi type is usually found in soil from multiple regions.
Who is mostly affected by the Valley fever?
In most cases, older people (over 60 years old) are diagnosed with this condition. It is caused by weakened immune systems that normally occur with aging. For more details, discuss it with your doctor.
What are the potential complications of the Valley fever?
Sometimes, people may develop complications of valley fever, especially without treatment. Check some of them below:
- Bone lesions
- Meningitis
- Severe lung infection
- Mental health problems
- Joint effusion
- Skin ulcers
- Increased sensitivity to light
Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.