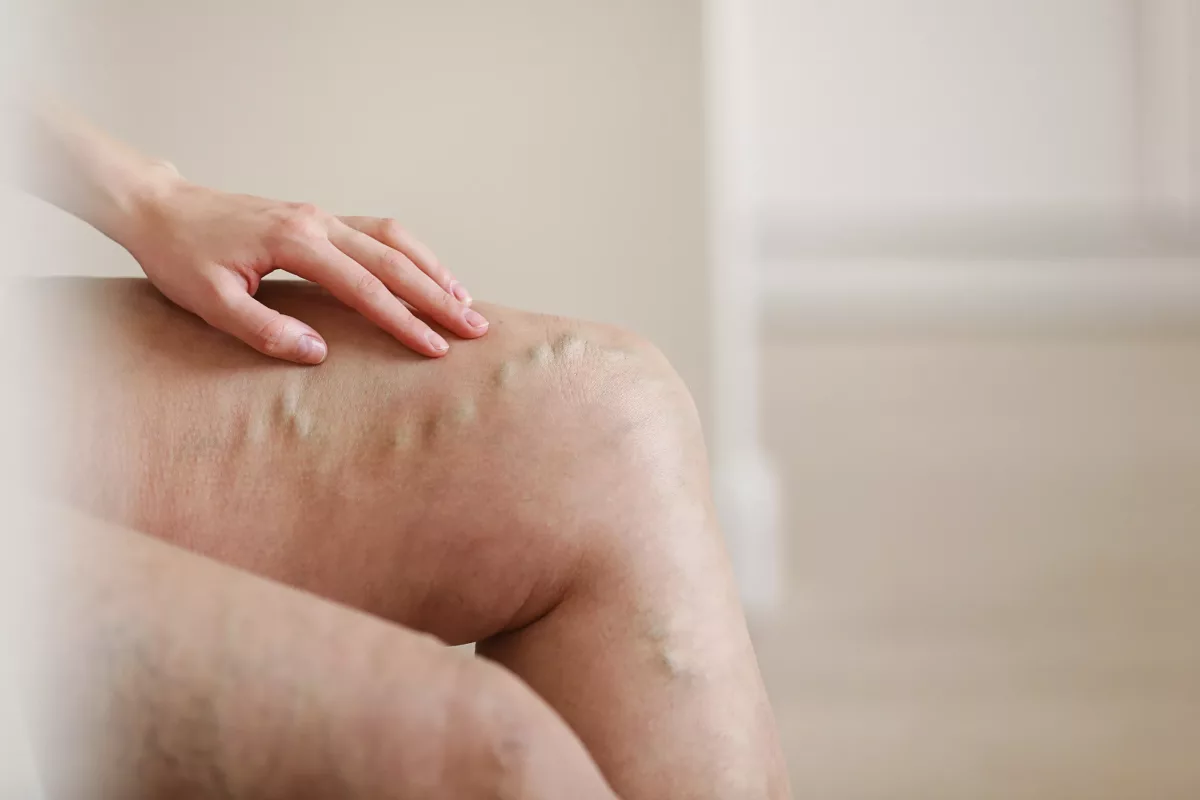
A very common health condition in which swelling of the veins under the skin in the legs, feet, or ankles occurs is called varicose veins. Usually, people develop this condition when the vein walls are weak and the valves are not working properly, which causes blood to back up in the vein. While there are some effective treatments, varicose veins may return. However, in most cases, this disease does not cause serious health problems.
Those who develop this disorder may notice blue or purple bulges in the legs, feet, or ankles. Moreover, people with varicose veins may experience itching, pain, and may notice certain spider veins (small red lines that appear close to the surface of the skin) that surround varicose veins.
Generally, this condition is not dangerous for people, but if a person develops a severe form of the condition, it may lead to serious health problems (such as blood clots). In mild cases, people usually get rid of symptoms with home remedies. However, if you have a severe form, physicians may prescribe injections, laser therapy, or surgery to treat it.
Symptoms
One of the most common symptoms is a blue or purple vein under the skin’s surface. However, some people with this condition may also experience other symptoms. For example:
- Bulging veins – These veins often appear on the legs, ankles, and feet.
- Heavy legs – In some cases, the muscles in the legs may feel tired, sluggish, or heavy, especially after physical activity.
- Itching
- Pain
- Muscle cramps
- Swelling
- Skin ulcers and discoloration – These symptoms often occur when you do not get treatment. In severe cases, people may experience venous ulcers on the skin.
In most cases, varicose veins develop on the lower part of the body (including calves, ankles, and feet). However, some people may develop this condition in the pelvic area (pelvic congestion syndrome), especially after pregnancy. Furthermore, hemorrhoids are also a form of varicose veins.
Causes
The primary cause of this condition is the weakened vein walls. Therefore, if blood pressure in these veins increases, they can become larger. However, when the vein stretches, the valves should keep the blood moving in one direction, which is not possible. As a result, the blood will back up in the vein, which causes it to bulge, twist, or swell. Usually, weakness of the vein walls occurs as a normal part of aging, standing for long periods, hormonal changes, or excessive body weight (obesity).
Risk Factors
While anyone may develop this disease, some people may be at increased risk of developing it due to certain factors. Check below some examples:
- Age – The walls of the veins can become weak as a normal part of aging. They also lose elasticity.
- Hormones – Some women are more prone to develop varicose veins due to hormonal changes that often happen during pregnancy, menopause, or the administration of birth control pills.
- Family history – If you have a parent or sibling with this condition, your risk of developing it significantly increases.
- Lifestyle choices – If you are standing or sitting for long periods, it may lead to reduced blood circulation, which increases the risk of varicose veins.
- Certain health conditions that cause hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Smoking
- Obesity
What Are The Potential Complications of Varicose Veins?
In most cases, this condition does not cause complications. If you develop a moderate or severe form of varicose veins and do not get treatment, it may lead to some complications, including bleeding, ulcers (open sores), inflammation and discoloration of the skin, chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), and others. CVI may also affect the heart’s function.
Furthermore, people with this disorder are at increased risk of developing blood clots. Thus, it is very important to get regular checkups to check for clotting diseases. For example:
- Superficial thrombophlebitis – This condition often occurs when blood clots appear in the varicose veins. While it often causes pain, it is not dangerous and mostly treatable.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) – In such cases, a blood clot develops in the deep veins.
- Pulmonary embolism – Usually, people develop this condition when a blood clot forms in the lung. Generally, this is a life-threatening condition that can be fatal without immediate treatment.
This document does not contain all possible complications of varicose veins. Moreover, you can talk with your healthcare professional about ways to reduce the risk or prevent these complications.
How to Prevent Varicose Veins?
In general, it is not possible to prevent this condition, but there are some steps to reduce the risk. Check below some examples:
- Do not stand or sit for long periods – You should perform regular physical exercise to encourage blood flow.
- Raise your legs – It often helps blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Try to get and maintain a healthy weight
- Stop smoking – If you face problems with smoking cessation, discuss it with your physician.
- Compression stockings – This option helps blood circulate, which may help prevent the worsening of varicose veins.
- You should wear clothes that fit properly
Diagnosis
Usually, physicians diagnose this condition during a physical examination because these veins are easy to see. However, they may ask some questions about the symptoms and medical history. In some cases, doctors may perform some imaging tests (such as an ultrasound) to check for complications (such as blood clots). The images produced during an ultrasound may also determine how well the valves work.
Treatment
While there is no way to cure this condition, treatment focuses on relieving the symptoms, preventing complications, and improving your quality of life. Check below some treatments often recommended by doctors for people with varicose veins:
- Elevation – It is recommended to raise your legs above the waist 2-3 times per day to improve blood flow and reduce pressure in the veins.
- Elastic stockings (also known as supportive stockings) – These socks help compress the veins to reduce discomfort.
- Sclerotherapy (injection therapy) – During this treatment, physicians will inject a specific solution into a vein.
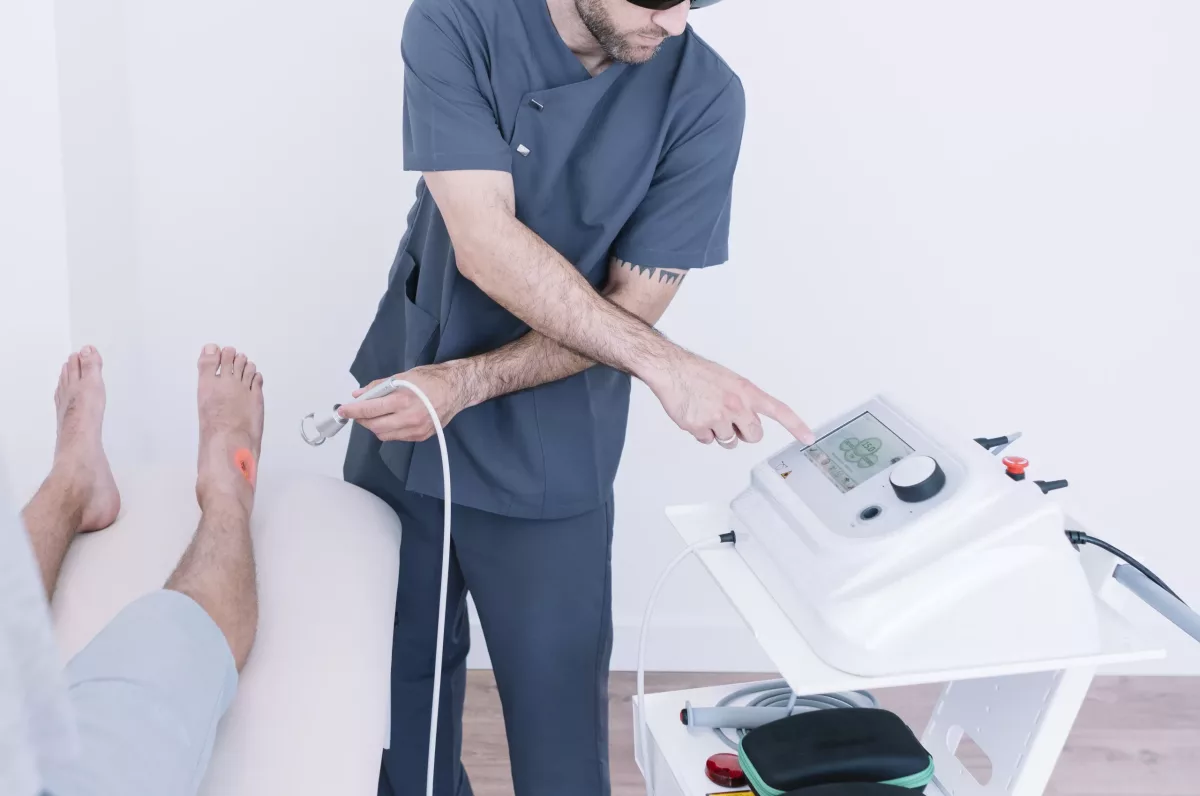
- Laser therapy – This treatment option is a minimally invasive procedure in which doctors use a long and small tube (catheter) and laser to close a damaged vein. This procedure is also known as endovenous thermal ablation.
- Ambulatory phlebectomy – During this procedure, doctors will make several cuts or punctures in the skin next to a varicose vein. Thus, they will tie off and remove one vein’s section.
- Vein surgery – This procedure is also known as ligation and stripping. During this treatment, surgeons often tie off or remove the affected vein, which helps stop blood from pooling.
However, previous treatments may cause some adverse reactions. For example:
- Bleeding
- Pain
- Infections
- Skin burns or numbness (rare)
- Scarring
- Damage to a nerve (rare)
- DVT
- Skin color changes
- Stroke (rare)
Frequently Asked Questions
Do varicose veins return after treatment?
Yes, especially if you become pregnant after treatment. Obese people are also at increased risk of developing recurrent varicose veins. For more details, discuss it with your doctor.
Will varicose veins go away?
In most cases, if this condition appears during pregnancy, it will go away on its own within 2-3 weeks after delivery.
When should I go to the ER?
Go to the nearest emergency room (ER) or call 911 in the U.S. if a varicose vein begins to bleed heavily. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any other questions.