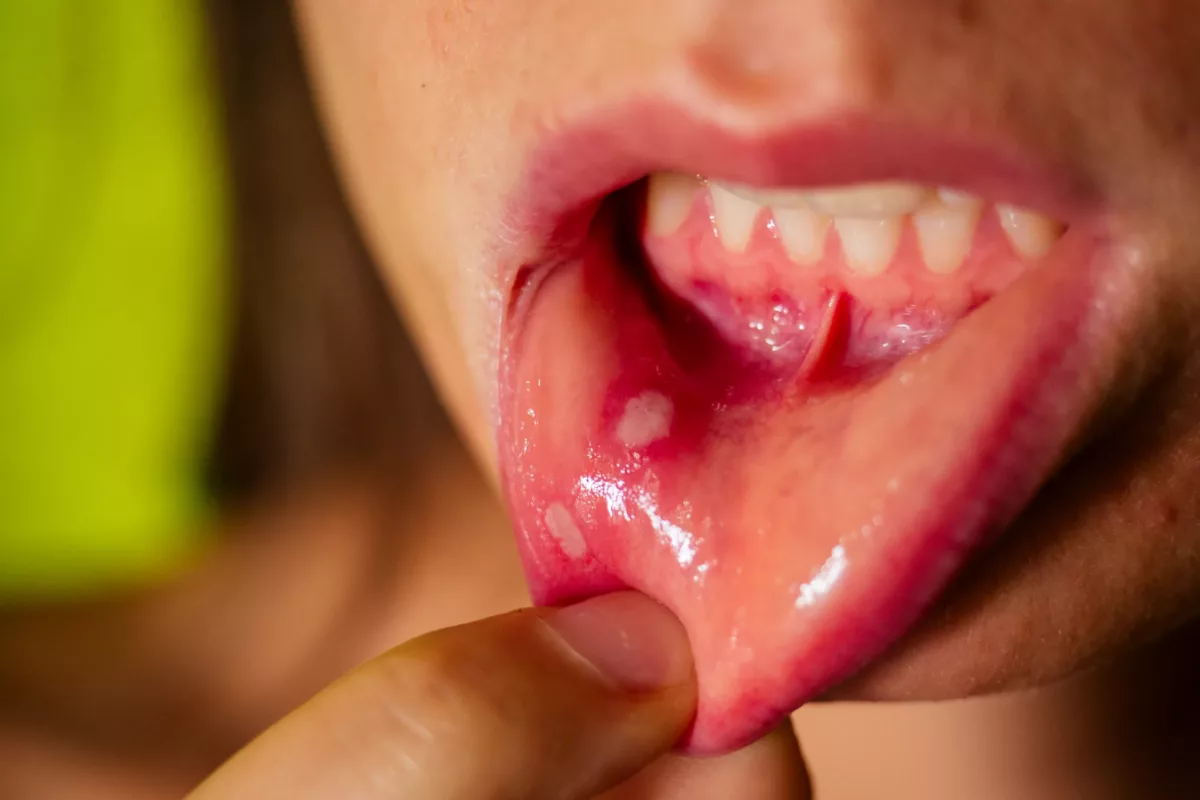
A disease in which the fungus called Candida albicans builds up in the mouth is called oral thrush or candidiasis. However, candida (a yeast) lives in the mouth naturally. In some cases, it may grow and begin to cause symptoms.
This condition causes creamy white patches or spots on the tongue or inner cheeks. In some cases, candidiasis may spread to the gums, tonsils, the roof of the mouth, or the throat back. While anyone may experience this condition, it mostly occurs in babies and older adults due to their weak immunity or certain health problems. Furthermore, some medicines may also increase your risk of developing this condition. Generally, this is not a serious condition, but if you have a weakened immune system, it may cause serious problems.
Symptoms
The symptoms appear depending on your age, overall health, and other factors. Check below some examples:
Children and Adults
- Creamy white patches or spots
- Raised patches that look similar to cottage cheese
- Burning, soreness, or redness that may cause swallowing or eating problems
- Bleeding
- Redness and cracking at the mouth corners
- Taste loss
- Irritation, redness, and pain under the dentures
In people with cancer or a weakened immune system caused by HIV/AIDS, the condition may spread to the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth with the stomach). In such cases, it is called Candida esophagitis and it may lead to swallowing problems, pain, and feelings that the food is stuck in the throat.
Babies and Breastfeeding Mothers
Babies may experience irritation and trouble feeding along with distinctive white spots in the mouth. Moreover, they can pass the infection to their mother during breastfeeding. Thereafter, the same infection may return to the baby. Check below some symptoms that females with infected breasts often experience:
- Cracked, itchy, sensitive, or red nipples
- Shiny or flaky skin on the areola (the area around the nipples)
- Pain
- Stabbing pains within the breast
If you notice that your child or you develop white spots in the mouth, tongue, or inside cheeks, do not hesitate to see a doctor.
Causes
In normal circumstances, immunity works to destroy germs and other invaders (such as viruses, fungi, and bacteria). As a result, it maintains the balance between “good” and “bad” body microbes. However, in some cases, the immune system fails and the fungus begins to grow causing this condition. Commonly, people are diagnosed with Candida albicans, which is the most common type.
Risk Factors
Healthcare professionals have identified some factors that may elevate your risk of developing oral thrush. These include:
- Weakened immune system – Candidiasis occurs commonly in babies and older adults because of lower immunity. However, some health conditions and treatments may cause a weakened immune system. For example cancer and its treatments (such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and others), organ transplant, certain medicines, HIV/AIDS, and others.
- Diabetes – In people with this condition who do not treat and control it, there is an increased risk of developing oral thrush. It usually occurs due to sugar that causes candida to grow.
- Vaginal yeast infections – However, the fungus that causes vaginal yeast infection and oral thrush are the same. Therefore, you can pass the infection to the baby.
- Certain medications – For example, Prednisone, inhaled corticosteroids, some antibiotics, and others. Previous medicines may disturb the natural balance of the body’s microorganisms. As a result, the risk of developing candidiasis increases.
- Other oral conditions – People who wear dentures (especially the upper ones) or have conditions that cause dry mouth also are at increased risk of developing oral thrush.
Complications
In most cases, this is a mild condition that does not cause major problems, especially for healthy children and adults. However, for people who follow cancer treatments or have HIV/AIDS, candidiasis may be more serious. Without treatment, it may lead to a serious infection called systemic candida infection.
How to Prevent Oral Thrush?
The following measures may help reduce the risk or even avoid candidiasis. For example:
- Rinse regularly the mouth, especially if you use a corticosteroid inhaler.
- Brush your teeth at least twice daily
- Floss daily
- Have regular dental checkups to ensure your dentures fit properly and do not cause problems (such as irritation).
- It is advised to limit the amount of sugar you eat.
- Regularly check your blood sugar if you have diabetes
- Treat existing health problems associated with oral thrush (for example vaginal yeast infection, dry mouth, and others).
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of the condition occurs differently among people because it depends if the infection has spread to other body parts (such as the esophagus). Physicians usually perform a mouth examination for abnormalities linked with oral thrush. They also may take a small sample of the affected area and test it under a microscope. Blood tests also are frequently done to check for underlying conditions.
However, if the candidiasis spreads to the esophagus, doctors may perform additional tests. These include:
- Endoscopic examination – During this test, doctors use an endoscope (a long and flexible tube with a lighted camera on the end) to check your esophagus for oral thrush symptoms. However, this test can be used to examine the stomach and the beginning of the small bowel.
- Biopsy – During previous examination, doctors may remove a small sample of the affected tissue and test it in the laboratory.
- Other tests – If the biopsy confirms the condition, physicians may perform additional tests to check for the underlying condition.
Treatment
The treatment for candidiasis often is different among patients because it depends on whether the infection spreads, your age and preferences, existing health conditions, and others. Check below some treatments usually recommended for people with oral thrush:
- Healthy children and adults – In such cases, physicians prescribe antifungal medicines that come in multiple forms such as lozenges, tablets, or liquids. Sometimes, physicians may recommend other medicines that work throughout the body if previous ones are not effective.
- Babies and nursing mothers – Physicians usually recommend mild antifungal medicines and regular antifungal creams for your breasts.
- Adults with weakened immunity – Healthcare professionals usually prescribe strong systemic antifungal medicines (such as Fluconazole, Itraconazole, and others) to treat candidiasis.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is oral thrush a sexually transmitted disease?
No, but it may be triggered by sex or passed during sexual activity. This infection is caused by a fungus called Candida albicans.
What conditions are mistaken for oral thrush?
Sometimes, candidiasis is mistaken for other health conditions. For example leukoplakia, oral lichen planus, geographic tongue, frictional keratosis, canker sores, and torus among others. For more details, discuss it with your doctor.
What are the possible oral thrush complications?
People with oral thrush may experience some complications, especially if they do not treat it. These include:
- Esophagitis
- Systemic infection
- Meningitis
- Endocarditis
- Arthritis
- Leaky gut syndrome
- Endophthalmitis
Talk with your doctor about ways to reduce the risk or prevent complications. If you have additional questions, ask your healthcare provider.