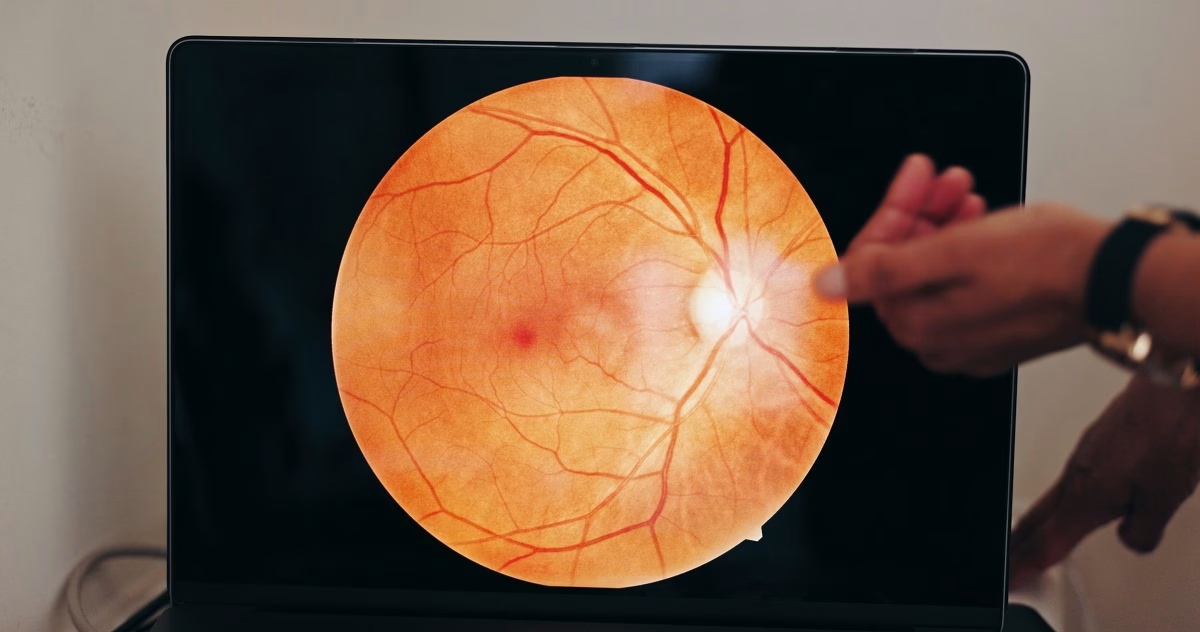
A health condition in which the child’s optic nerve does not develop properly is called optic nerve hypoplasia (ONH). This condition may also affect the pituitary gland and the connection between the 2 halves of the brain. If your child develops a more severe form of optic nerve hypoplasia, it may lead to blindness (permanent vision loss) or vision impairment. However, there are several treatment options to address the child’s symptoms.
Furthermore, ONH is a congenital (present at birth) condition in which the optic nerve is small or underdeveloped. This nerve is responsible for sending signals between the eyes and the brain. In addition to vision problems, this condition may also affect certain parts of the brain. For example:
- Midline brain abnormalities – Certain tissues in the brain may also not develop properly due to ONH. These include the septum pellucidum and corpus callosum, which are nerve fibers that separate the brain evenly.
- Pituitary gland hypoplasia – This gland is located at the base of the brain (below the hypothalamus), and it regulates multiple bodily functions, such as hormone production. Abnormalities in the pituitary gland may lead to reduced hormone production.
In some cases, this disorder is identified as septo-optic dysplasia (SOD or de Morsier syndrome). That’s why research shows all cases of SOD affect the optic nerve development, but only 10% of ONHs impact the midline brain (septum pellucidum) development.
This condition occurs rarely and affects about 1 in 10,000 children in the U.S. On the other hand, ONH is the leading cause of blindness in children under 3 years old in the U.S.
Symptoms
The symptoms often appear differently among people with optic nerve hypoplasia. It depends on the severity of the condition, whether it affects one or both eyes, existing health problems, and age. Check below some symptoms of optic nerve hypoplasia:
- Nystagmus (fast eye movement)
- Visual impairment
- Strabismus (crossed eyes)
- Esotropia (eye misalignment)
- Difficulty focusing on objects
When the condition affects the pituitary gland, you may experience additional symptoms. For example:
- Difficulty regulating multiple body functions, such as thirst, hunger, sleep, and body temperature
- Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid gland)
- Delayed sexual maturation
- Diabetes insipidus
- Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
- Jaundice (yellowing of the eyes and skin)
- Reduced growth and short stature
If you develop midline or other brain development irregularities, you may experience intellectual disability (cognitive development problems) or seizures. Immediately contact your healthcare professional if you experience any of the previous symptoms.
Does Optic Nerve Hypoplasia Cause Blindness?
While some people may develop this condition with mild symptoms that may improve over time, in more severe cases, people may experience severe vision impairment and even blindness. Usually, doctors can tell how this disorder affects your child’s vision.
Causes
Healthcare providers do not fully understand what causes optic nerve hypoplasia. However, they believe it occurs due to a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Sometimes, ONH may occur due to fetal alcohol syndrome.
While not all cases have a genetic component, some studies have shown that there are some rare genetic mutations that can contribute to ONH. These abnormal genes often pass from the biological parents to their children during pregnancy (autosomal recessive pattern). Check below some examples:
- HESX1
- SOX2 and SOX3
- OTX2
- PROKR2
Risk Factors
While doctors do not know the exact cause of ONH, they have identified some factors that may increase your risk of developing it. Examples include:
- Age – If you are under 19 years old, the risk of developing ONH increases.
- First pregnancy
- Family history of ONH – If you have a parent or sibling with this condition, your risk of developing it significantly increases.
- Gestational diabetes
- Premature birth or low birth weight
- Maternal smoking
- Low maternal weight gain
What Are The Potential Complications of Optic Nerve Hypoplasia?
People who develop ONH may also experience some complications, especially if they do not get treatment. Check below some examples:
- Difficult regulating body temperature
- Hyperphagia (strong hunger and thirst)
- Obesity
- Abnormal sleep/wake cycles
- Hypophagia (limit food intake) and food aversion
- Developmental delay (including motor and communication skills)
- ASD (autism spectrum disorder)
- Vision disorders (including poor visual acuity, strabismus, nystagmus, amblyopia, and others)
- Hypopituitarism (reduced hormone production by the pituitary gland)
- Seizures
- Hypothalamic dysfunction
This article does contain a complete list of ONH complications. However, you can consult with your healthcare professional about ways to reduce the risk of developing them. In addition, this disorder cannot be prevented because it occurs during conception. You can perform some genetic tests to make sure you and your partner do not have genetic mutations linked to ONH before pregnancy.
Diagnosis
When doctors suspect ONH, they often refer the patients to ophthalmologists. Therefore, they will perform an eye examination to check for abnormalities linked to the disease. In most cases, the first sign of ONH is abnormal eye movement. It usually appears in children within the first months of life.
Sometimes, this condition may occur alone without affecting parts of the brain. In such cases, the disease is confirmed with one or two additional developmental problems outside the optic nerve. For example, pituitary gland and brain irregularities. Commonly, to confirm this condition, doctors often perform the following tests. For example, MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans and CT (computerized tomography) scans. In some cases, physicians may also perform blood tests to rule out other disorders that cause similar symptoms to ONH.
Treatment
Unfortunately, there is no way to cure this condition because congenital disorders cannot be reversed or restored. That’s why the treatment goal is to relieve the symptoms, reduce the progression of the disease, and improve your quality of life. Check below some treatments often recommended by doctors for people with ONH:
- Vision therapy (it includes low-vision aids, such as glasses or magnifiers)
- Hormone replacement therapy (medicines)
- Occupational, speech, and physical therapies
Usually, doctors make an individual treatment plan to manage this condition.
Frequently Asked Questions
When should I see a healthcare provider?
If you notice that your child’s eyes do not follow you, cross, or move unusually, immediately contact your healthcare professional. You should also go to the nearest emergency room (ER) or call 911 if your child has a seizure.
Is optic nerve hypoplasia serious?
In some cases, people may develop a severe form of this condition that causes serious vision issues and other health problems. When the disease also affects the pituitary gland, your child may experience life-threatening symptoms.
What eye conditions are linked to autism?
Examples include refractive errors, strabismus (crossed eyes), and amblyopia (lazy eye). Some people with autism may also have problems with tracking or moving objects and light sensitivity. The most common treatments include glasses and vision therapy. Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.