If your thyroid gland produces an increased amount of thyroid hormone, it is a condition called overactive thyroid or hyperthyroidism. The most common overactive thyroid symptoms are weight loss, increased appetite, anxiety, and fast heartbeat. Thus, this condition makes your metabolism speed up. Furthermore, hyperthyroidism can be treated with the following medicines including beta-blockers, radioactive iodine, surgery, and antithyroid medicines.
What is Hyperthyroidism?
This thyroid disease happens when the thyroid gland produces and releases increased levels of T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) hormones. It is not recommended to ignore this condition and visit a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
The thyroid gland is located in the front of the neck. However, the human body has different glands (organs), which are located throughout the body. The thyroid gland plays an important role in different body processes. For example:
- Keep under control body temperature
- Controlling heart rate and metabolism
The body is balanced (which means all body functions work well) if the thyroid gland works properly but if not this gland may produce too much or too little thyroid hormones. This effect usually leads to certain health problems.
What is The Difference between Underactive Thyroid and Overactive Thyroid?
Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) are both thyroid diseases that should be treated by a healthcare professional. The only difference between them is the amount of produced hormones. Hence, hypothyroidism happens when the thyroid gland creates less hormones than the body needs and hyperthyroidism is a condition in which a person has increased hormone levels (more than is needed).
How Common is Hyperthyroidism?
This is considered a rare health condition that affects roughly 1% of the population in the U.S. However, hyperthyroidism is diagnosed mostly in females and people assigned to females at birth (AFAB).
Symptoms
The symptoms often fluctuate among people. It depends on the severity of the condition, other existing diseases, medicines, your age, and others. Check below some examples:
- Palpitations (fast heartbeat)
- Weight loss
- Feeling nervous or shaky
- Increased appetite
- Diarrhea
- Vision changes
- Moist, warm, and thin skin
- Menstrual changes
- Excessive sweating
- Heat intolerance
- Bulging of the eyes
- Muscle weakness
- Hair loss
- Enlargement and swelling of the neck (caused by enlarged thyroid gland)
If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, do not hesitate to consult your doctor.
Causes
- Graves’ Disease – It is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s defense (immune system) attacks the thyroid gland. Graves’ disease usually begins in families (hereditary). This condition is considered one of the most common causes of hyperthyroidism which accounts for about 85% of all overactive thyroid cases.
- Thyroid Nodules – A lump or growth of cells in the thyroid gland is called thyroid nodules and also can provoke hyperthyroidism.
- Thyroiditis – An inflammation of the thyroid gland causes a condition called thyroiditis. This condition can be painful or painless. It may happen to a person within a year after delivering a baby (postpartum thyroiditis).
- Excess Iodine – If you are taking an increased amount of iodine, either through diet or medicines, you are at higher risk of developing an overactive thyroid gland. For example, receiving intravenous iodinated contrast and drugs (such as Amiodarone) can provoke hyperthyroidism.
Ask your healthcare professional if you have any questions.
Diagnosis
There are three ways to diagnose this health condition. For example:
- Imaging tests (used to look at your thyroid gland)
- Blood tests (help to determine hormone levels)
- Physical examination (a doctor verifies if your thyroid gland is enlarged)
Imaging Tests
The following tests usually help the doctor to diagnose hyperthyroidism or the potential cause. Check below some examples:
- Radioactive Iodine Uptake (RAIU) Test – The patient takes a small dose of radioactive iodine also known as radiotracer by mouth. Thus, after 6-24 hours your healthcare professional will scan the thyroid gland to determine how much radioactive iodine has absorbed your thyroid gland. As a result, if your thyroid absorbs an increased amount of radioactive iodine, it means your gland is creating too much T4 (thyroxine) hormone. In such cases, a person usually experiences Graves’ disease or thyroid nodules.
- Thyroid Scan – This test is very similar to the previous but it also uses a gamma camera to take some images of your thyroid gland and radioactive iodine appears “bright” on the screen. This test also can be used to determine whether you have thyroid nodules or lumps, inflammation, swelling, goiter, or thyroid cancer or not.
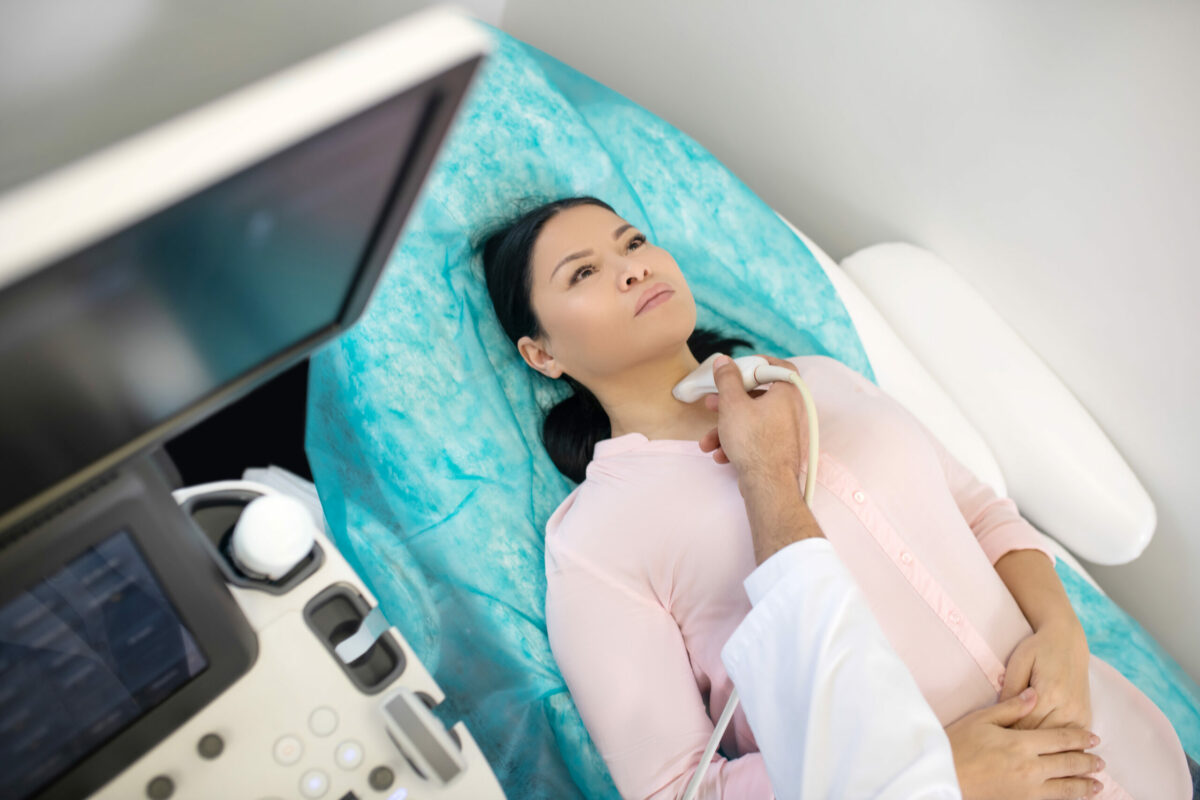
- Thyroid Ultrasound – This procedure involves high-frequency sound waves to make thyroid images.
Blood Tests
Your doctor will take a sample of blood to verify for high levels of thyroid hormone.
Physical Examination
Check below what your doctor will verify during a physical examination:
- Thyroid – Physicians usually check if the thyroid gland is enlarged.
- Eyes – Your doctor will verify your eyes for redness, bulging, redness, and others.
- Heart – Doctors use a stethoscope to listen to the heart for irregular heartbeat.
- Hands – Your healthcare professional will check for nail changes and hand tremors.
- Skin – During this test, providers check if your skin is moist and warm.
Treatment
Fortunately, several treatment methods are available to treat hyperthyroidism. Examples include:
- Beta Blockers – Medicines that help to block the thyroid hormones action of the body. However, these drugs do not change hormonal levels in the blood. Using Beta Blockers can lessen symptoms including shakiness, nervousness, fast heartbeat, and others. These medications are usually used in combination with other hyperthyroidism treatments.
- Surgery – In some circumstances, your doctor may remove the thyroid gland which will help with hyperthyroidism. On the other hand, it will cause hypothyroidism, which leads to lifelong thyroid supplement use.
- Radioactive Iodine – In most cases, using medicines with radioactive iodine helps to shrink the thyroid gland by damaging cells that provoke enlargement. This effect leads to a decrease in hormone levels. However, this medicine causes permanent damage to the thyroid gland but cures hyperthyroidism. In addition, people who get this treatment option will administer thyroid hormone medications for the rest of their lives.
- Antithyroid Drugs – Physicians may prescribe Methimazole or Propylthiouracil to block the hormone production by the thyroid gland.
If suspect you have hyperthyroidism, visit a doctor right away.
Risk Factors
- Family history of thyroid disease
- Medical history, including pernicious anemia, type 1 diabetes, and primary adrenal insufficiency (Addison’s disease).
- Your diet contains an increased amount of iodine.
- Pregnancy
Complications
One serious hyperthyroidism complication is thyroid storm also known as thyroid crisis or thyrotoxic crisis. It usually occurs when your thyroid gland produces high levels of thyroid hormone in short periods. While this complication is very rare it is life-threatening. In case you experience the following symptoms, immediately visit a doctor. Examples include:
- Delirium
- Congestive heart failure
- Loss of consciousness
- Agitation, irritation, or anxiety
- Fast heartbeat (tachycardia)
- High fever
Additionally, a common Graves’ disease complication is Graves’ eye disease. This condition cannot be prevented and it provokes the following symptoms. For example:
- Vision loss
- Double vision
- Bulging eyes
- Sensitivity to light
Frequently Asked Questions
Is hyperthyroidism a curable condition?
Yes, a removal of the thyroid gland can cure an overactive thyroid gland. Thereafter, you should get thyroid supplements for the rest of your life. This will help to maintain normal thyroid hormone levels. Otherwise, you will experience hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid gland).
What can happen if hyperthyroidism is untreated?
Check below for some examples of what can happen if this condition is not treated:
- Stroke
- Congestive heart failure
- Osteoporosis
- Atrial fibrillation
Can hyperthyroidism provoke female infertility?
Hyperthyroidism can provoke irregular menstrual cycles. Therefore, this symptom can lead to problems with becoming pregnant.