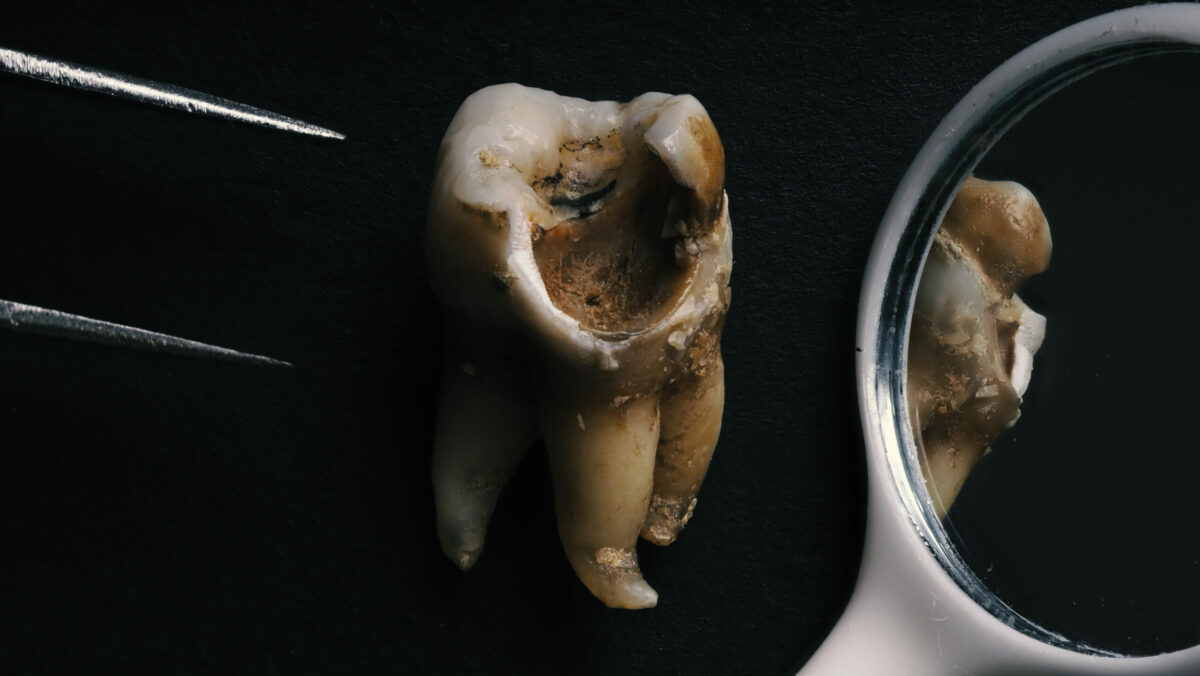
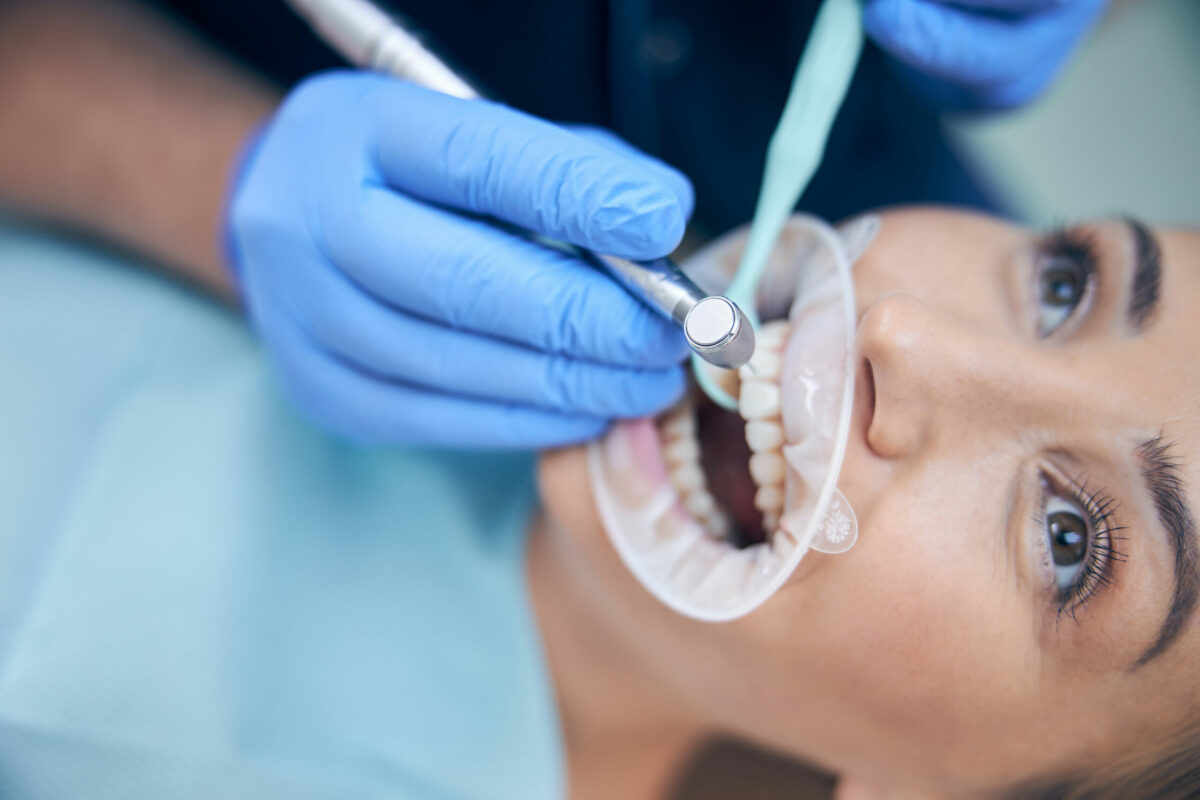
Areas with hard surfaces of the teeth that are damaged are called cavities. Generally, the regions of tooth decay become small holes and openings that may cause serious infections, toothache, or even tooth loss. These cavities usually occur due to large amounts of sugary drinks, smacking a lot, bacteria in the mouth, or poor dental cleaning.
Tooth decay and cavities are common health problems in the world, especially in children, teenagers, and older adults. However, anyone who has teeth may develop cavities (including babies).
People who ignore the symptoms and do not treat the condition may experience some complications because cavities become larger and may negatively affect the deep layers of the teeth. However, regular dental examinations and good dental cleaning may protect you from cavities.
Symptoms
The symptoms of cavities depend on several factors. For example the amount and location of cavities, existing health problems, and others. Check below some symptoms that people with cavities usually experience:
- Toothache
- Pain
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Mild to severe pain, especially while eating or drinking something sweet, cold, or hot
- Pits and holes in the teeth
- Black, white, or brown staining on any surface of a tooth
In most cases, people do not know they have cavities. That’s why regular dental examinations are recommended. However, immediately visit a doctor if toothache or mouth pain occurs.
Causes
The process that causes cavities usually develops slowly over time. Generally, tooth decay causes cavities. Check below how tooth decay occurs:
- Plaque forms – The plaques that appear on the teeth are made from eating a lot of sugar and poor dental cleaning. Furthermore, uncleaned plaques may harden and transform into tartar if are not cleaned.
- Plaque attacks – The bacteria that grow on the teeth produce acids that destroy minerals found in the outer enamel of the teeth. After the enamel is worn away, the bacteria can spread to the next teeth layer (dentin). However, the next layer is softer and less resistant to the acid that bacteria produce.
- Further damage – However, when tooth decay occurs, the bacteria continue to move to the inner tooth layers. This tooth part contains blood vessels and nerves, and when the bacteria reaches these layers of the teeth, you may experience inflammation and irritation.
Risk Factors
Generally, cavities may affect anyone. Physicians identified some factors that could increase your risk of developing teeth problems. Examples include:
- Location of the tooth – In most cases, tooth decay occurs in the back teeth (including molars and premolars). It happens because these teeth have multiple grooves, pits, crannies, and roots where small food pieces collect easily. Moreover, back teeth are hard to clean properly, which also increases the risk of tooth decay.
- Some drinks and foods – There are some foods that cling to your teeth easily and stay for long periods. As a result, the risk of tooth decay increases significantly. For example, milk, ice cream, honey, sugar, soda, dried fruits, cake, cookies, and others.
- High amounts of snacks or sugary drinks – The mouth bacteria begin to produce increased acid levels when snaking or sipping a lot of sugary drinks. This acid may damage the enamel of the tooth and even go to the deep tooth layers.
- Bedtime baby feeding – It is not advised to give babies drinks that contain milk, formula, juice, or other liquids that contain sugar at bedtime because these beverages remain on teeth and feed the bacteria.
- Poor dental cleaning – Those who do not clean their teeth at least two times per day (in the morning and before bedtime) are more likely to develop cavities.
- Decreased Fluoride levels – This is a mineral that helps prevent cavities. If you are not getting it enough, the risk of developing cavities also increases. Public water, mouth rinses, and toothpaste contain this mineral. However, bottled water often does not contain Fluoride.
- Age – Cavities are common in the U.S., especially in young children and older adults. Without treatment, these teeth problems may lead to gum problems.
- Dry mouth – Lack of saliva causes this risk factor. Thus, it also elevates the risk of developing cavities. Furthermore, substances found in saliva may help counter the acid made by bacteria.
- Dental fillings or devices
- Heartburn – This is one of the most common symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Heartburn may cause damage to the enamel of the teeth and cause serious damage. It also allows the bacteria to produce a lot of acids that usually lead to tooth decay.
- Eating disorders – Bulimia, anorexia, and other eating disorders may cause teeth problems (including cavities).
Complications
Many people do not take cavities seriously or think that it is not important if children or babies develop cavities. However, this is a serious condition that requires treatment. Otherwise, it may lead to serious and long-lasting complications. Check some of them below:
- Chronic pain
- Abscess (an infection caused by bacteria that causes a pocket of pus that forms in the tooth)
- Pus or swelling (inflammation) around the teeth
- Problems with chewing
- Tooth loss that may negatively affect confidence and self-esteem
- Life-threatening infections (rarely)
- Weight loss or nutrition problems caused by pain and chewing problems
How to Prevent Cavities and Tooth Decay?
Generally, good dental hygiene can reduce the risk of developing cavities. Check below some tips that may help prevent them:
- Brush your teeth with toothpaste that contains Fluoride, especially after eating or drinking.
- Regularly rinse your mouth
- Get dental examinations regularly
- You can use dental sealants (a protective plastic that is applied on the chewing surface of back teeth). It helps prevent food collection in those teeth.
- It is advised to drink some tap water because most of it contains Fluoride that helps prevent cavities.
- Limit snacking and sugary drinks because they feed the bacteria that produce acids.
- Add to your diet tooth-healthy foods (including fresh fruits, vegetables, unsweetened coffee and tea, and others)
- Discuss with your dentist about Fluoride treatments
Diagnosis
In most cases, dentists diagnose this condition in the following way. For example:
- Ask some questions about tooth pain or sensitivity
- Perform a dental examination to check for abnormalities linked with cavities
- Check your teeth by using X-rays
Imaging tests help doctors identify the cavities type you experience including a smooth surface, pit and fissure, or root.
Treatment
Early detection and proper treatment of cavities and other dental problems may prevent other, more serious infections. People who treat cavities that do not cause pain, usually do not require multiple treatments. Check below some of them:
- Fluoride treatments – This treatment contains more Fluoride than in tap water, toothpaste, or mouth rinses. It usually involves liquid, gel, foam, or varnish that is brushed onto the teeth.
- Fillings – In most cases, this is the primary treatment and it involves multiple materials.
- Crowns – The crown helps protect the affected tooth from fractures.
- Root canals – The treatment goal is to save a badly damaged or infected tooth instead of removing it and placing an artificial one. It usually is used when decay goes to the pulp (the inner tooth layers).
- Tooth extractions – Dentists recommend this treatment when a tooth is seriously decayed and cannot be repaired. Thereafter, you can consider a bridge or a dental implant to replace the missing one.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a cavity heal on its own?
No, once a cavity occurs, it does not go away on its own. However, in the early stages, you may treat the condition with good oral hygiene and Fluoride treatments.
What are the most common cavity symptoms?
These include:
- Toothache and pain
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Discoloration of the teeth
- Gum bleeding
- Bad breath or taste
- Facial swelling and pus in the mouth (in severe cases)
If any of the previous symptoms occur, immediately visit a dentist.
What happens if cavities are left untreated?
There are a lot of people who think cavities are not serious but they may cause serious complications if left untreated. For example:
- Serious or even life-threatening infections
- Tooth loss
- Abscesses
- Chronic pain
- Gum disease
This article does not contain all possible cavities complications. Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.