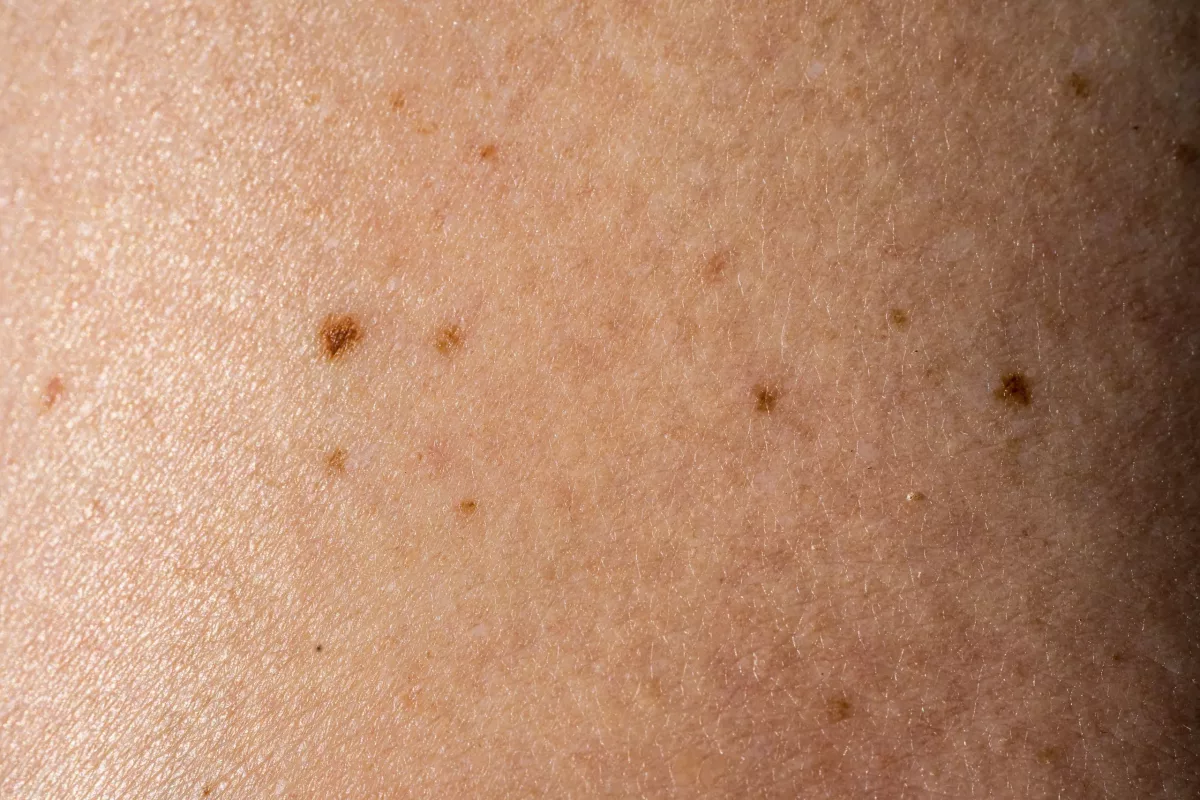
Small and dark areas on the skin are called age spots (also known as liver spots). These spots usually vary in size and mostly appear in areas that are continuously exposed to the sun. For example, the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. Sometimes, age spots are called sunspots or solar lentigines.
These spots are very common in older adults (over 50 years old). However, younger people may also get them if they spend a lot of time in the sun.
Some age spots may look like cancerous growths. However, these spots do not require treatment, but they indicate the skin has gotten a lot of damage and is trying to protect itself from further damage. To prevent age spots, you should use sunscreen or avoid the sun regularly. However, there are some procedures that can lighten or remove these spots.
Symptoms
Generally, these spots can appear on any type of skin, but mostly appear in adults with light skin. While freckles fade with no sun exposure, liver spots do not fade. Age spots:
- Are often tan to dark brown, flat or oval areas of increased pigmentation
- Can group together
- Range in size to about ½ inch (13 millimeters) across
- Appear usually on the skin that has been exposed to the sun over the years (including the back of the hands, top of the feet, face, shoulders, and upper back)
While liver spots do not need treatment, you should see a doctor if you notice the following changes. For example:
- A spot is black or increasing in size
- Spots have an irregular border or unusual color combination
- Bleeding
Previous symptoms may indicate melanoma.
Causes
The primary cause of age spots is overactive pigment cells. Normally, ultraviolet (UV) light increases the production of melanin (a natural pigment that gives the skin its color). When the skin is exposed to the sun for many years, melanin becomes clumped or is made in high concentrations, which causes age spots to appear.
Furthermore, some people may develop age spots due to commercial tanning lamps and beds.
There are some factors that could increase your risk of developing age spots. For example, light skin, a history of intense or frequent sun exposure, or sunburn.
How to Prevent Age Spots?
Check below some tips that may help avoid age spots. For example:
- Avoid exposure to the sun between 10 a.m. and 2 p.m. because, during this time, the sun’s rays are more intense.
- Regularly use sunscreen – It is recommended to use a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30 when outdoors.
- Use protective clothing – You should wear clothes that cover the arms and legs to protect them from direct sunlight.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of the age spots usually involves the following tests and examinations. For example:
- A physical examination – In most cases, a physical examination is enough to diagnose age spots. However, when doctors suspect you may have other skin disorders, they may perform a biopsy.
- Skin biopsy – This is a specific test in which doctors will get a small sample of the affected tissue to test it in the laboratory. It helps determine skin cancer (such as lentigo maligna) and other skin conditions.
Treatment
For those who want to make age spots less noticeable, there are multiple treatments available to lighten or even remove them. Check below some examples:
- Medicines – Doctors may prescribe some topical medicines with Hydroquinone or Tretinoin that should be applied on the affected skin over a few months. It may help fade the spots. However, these medicines may cause some adverse reactions, such as itching, redness, burning, or dryness.
- Laser and intense pulsed light – There are some therapies that use laser or pulsed light to destroy melanin-producing cells (also called melanocytes) without causing damage to the skin.
- Cryotherapy (freezing) – This treatment option uses a cotton-tipped swab to apply nitrogen. It helps destroy extra pigment. The substance is often applied for five seconds or less. Doctors often recommend cryotherapy for people who have small groups of spots.
- Dermabrasion – To notice improvements, you should perform this procedure multiple times. It involves a rotating brush that sands down the surface layer of the skin. Thereafter, new skin grows instead. Potential adverse reactions include redness, scabbing, and swelling.
Other Treatments
- Microdermabrasion – This treatment option is similar to dermabrasion but is less aggressive. After treatment, you may notice mild skin blemishes with a smooth appearance only. However, to notice improvements, you need to perform this procedure for months.
- Chemical peel – It involves a chemical substance that removes the top layer of the skin, which allows new skin to grow instead. Scarring, infection, and lightening or darkening of the skin color are the most common adverse reactions of this treatment.
Usually, the age spot treatments are performed in a doctor’s office and do not require hospitalization. The duration of the treatment varies among people. All people should use protective clothing and an SPF of at least 30 after treatment.
Additionally, there are a lot of over-the-counter (OTC) creams and lotions used to lighten age spots. You can use a nonprescription fade cream with hydroquinone, glycolic acid, or kojic acid. However, topical products with hydroquinone may cause skin irritation. Consult with your healthcare professional before using any OTC creams and lotions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you get rid of age spots?
There are multiple treatment options used to get rid of age spots. For example, topical creams and lotions, laser treatments, cryotherapy, microdermabrasion, and chemical peels. If you do not know what the best option for you is, discuss it with your healthcare professional.
What vitamin are you lacking if you have age spots?
There are three vitamins responsible for lightening dark spots. For example, vitamin C, vitamin B12, and vitamin E. These vitamins help the skin produce more collagen and inhibit melanin.
Do liver spots mean liver problems?
Age spots are sometimes called liver spots, but that does not mean a person has liver problems.
What can be mistaken for age spots?
There are some health conditions that can be mistaken for age spots. For example:
- Freckles
- Moles
- Melasma
- Actinic keratosis
- Melanoma
Visit a doctor if you are not sure you have age spots. If you have additional questions, ask your healthcare provider.