A rare type of cancer that grows quite fast and negatively affects the skin and blood is called Sezary syndrome. Usually, when it occurs, the symptoms are very similar to eczema or other common skin disorders. Unfortunately, this condition cannot be cured, but with proper treatment, you can lessen the symptoms and improve your quality of life. Moreover, physicians may prescribe some additional treatments to prevent the spread from skin and blood to other structures and organs in the body.
In other words, this condition is a fast-growing type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. People with Sezary syndrome have cancerous T lymphocytes in the skin, bloodstream, and lymph nodes. This disorder may also cause skin color changes and a painful and itchy rash. However, there are multiple treatments that can relieve the symptoms of this type of cancer.
This syndrome occurs quite rarely and affects about 1 in 1 million people in the U.S.
Symptoms
While the most common symptoms include red rash (erythroderma), itching, and pain, people with Sezary syndrome may also experience other symptoms. In the early stages, this syndrome causes symptoms similar to eczema or psoriasis. When it advances, you may notice other symptoms, including small and raised bumps (also called papules). Check below for other symptoms of Sezary syndrome:
- Fever
- Extreme tiredness (fatigue)
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Ectropion (a condition in which the eyelids turn outward)
- Hair loss
- Unusual weight loss
- Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
- Edema (swelling in the lower legs)
- Reduced tolerance to cold
It is very important to get medical care if any of the previous symptoms occur.
Causes
This rare condition occurs due to genetic mutations (changes) that turn T-cells into abnormal cells. Therefore, these abnormal cells begin to multiply uncontrollably, which can affect the skin, lymph nodes, and bloodstream. Nowadays, healthcare providers do not know what exactly triggers these genetic mutations.
Risk Factors
While it is not possible to determine the exact cause of this syndrome, healthcare providers have identified some factors that may increase the risk of developing this rare syndrome. Check below some examples:
- Age – This condition is mostly diagnosed in older adults (over 60 years old).
- Sex – Males are more likely to develop this syndrome than females.
- Autoimmune disorders
- Race – Some research suggests that Black people are at increased risk of developing Sezary syndrome compared to other races.
- Chromosomal Abnormalities – People who experience Sezary syndrome also have chromosomal abnormalities, according to some recent studies.
What Are The Potential Complications of Sezary Syndrome?
This disorder may also cause some complications, especially if it is not treated. Examples include:
- Increased risk for other types of lymphoma or infections
- Metastatic cancer (this type of cancer may spread to other parts of the body, including bone marrow, spleen, liver, and lungs)
- Lymph node enlargement
- Autoimmune conditions
This article does not contain a full list of complications. However, you can talk with your healthcare professional about ways to reduce the risk or prevent previous complications.
Diagnosis
In most cases, the diagnosis of this syndrome begins with a physical examination to check for irregularities linked to the disease. Thereafter, doctors may ask some questions about the symptoms and family history. However, to confirm the disease, physicians may perform the following tests. They also help rule out other diseases that cause similar symptoms. Check some tests below:
- Blood tests – Doctors often perform a complete blood count (CBC) with differential to check the number of Sezary cells in the blood and a peripheral blood smear.
- Biopsy – This procedure involves the removal of a small sample of the affected tissue for testing under a microscope to check for cancerous cells. In most cases, doctors perform biopsies of the skin, lymph nodes, or bone marrow.
- Imaging tests – The following tests are often done to determine the extent (stage) of the cancer. For example, chest X-ray, CT (computed tomography) scans, and PET (positron emission tomography) scans.
Treatment
Usually, doctors prescribe different treatments for people with Sezary syndrome because they depend on several factors. For example, the severity of the cancer, overall health, age, and preferences. Check below some treatments often recommended for people with this syndrome:
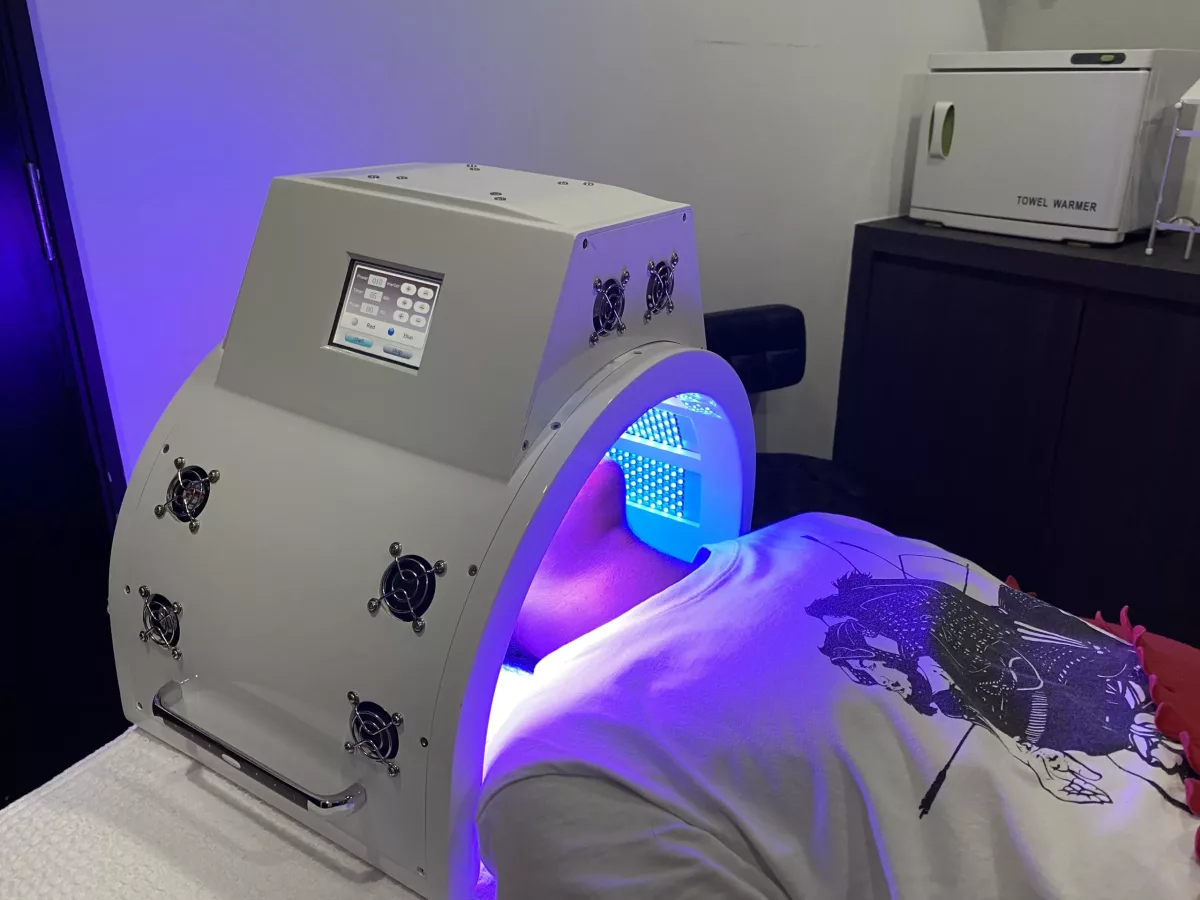
- Phototherapy – In some cases, doctors may recommend extracorporeal photopheresis. This procedure involves collecting the white blood cells (leukapheresis) and exposing them to ultraviolet (UV) light.
- Radiation therapy – This treatment uses powerful energy beams to destroy cancerous cells. This energy often comes from X-rays or protons, but may also come from other sources.
- Chemotherapy – This treatment involves strong medications to kill cancer cells throughout the body. While most people receive intravenous (IV) medicines, a pill form is also available. This treatment can be recommended by doctors along with radiation therapy, before surgery to shrink a large tumor, or after surgery to destroy cancerous cells that may remain.
- Targeted therapy – Usually, physicians recommend a type of targeted therapy called monoclonal antibody therapy.
- Immunotherapy – This treatment involves specific medications that help boost the immune system to find and destroy cancerous cells. In most cases, physicians recommend interferon. Furthermore, cancer cells often produce specific substances that help them evade detection by the immune system. Immunotherapy is often prescribed by doctors in advanced stages of cancer or when other treatments are not effective.
- Other medicines – Healthcare professionals may also prescribe corticosteroids, retinoid creams or gels (such as Bexarotene) to relieve the symptoms caused by Sezary syndrome.
In addition, almost all cancer treatments have adverse reactions. These include extreme tiredness (fatigue), nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and others. For more details, discuss it with your healthcare professional.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Sezary syndrome be cured?
Unfortunately, there is no way to cure this syndrome. That’s why the treatment goal is to ease the symptoms and improve your quality of life. Physicians may also prescribe additional treatment to prevent it from spreading to other structures and organs in the body.
How long does Sezary syndrome last?
This is a chronic health condition, which means you may need treatment for the rest of your life.
What is the life expectancy of someone with Sezary syndrome?
Almost all people with Sezary syndrome survive an average of 2 to 4 years, especially if it occurs in an older adult (over 60 years old). However, the survival rate has improved with some new treatments. Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.