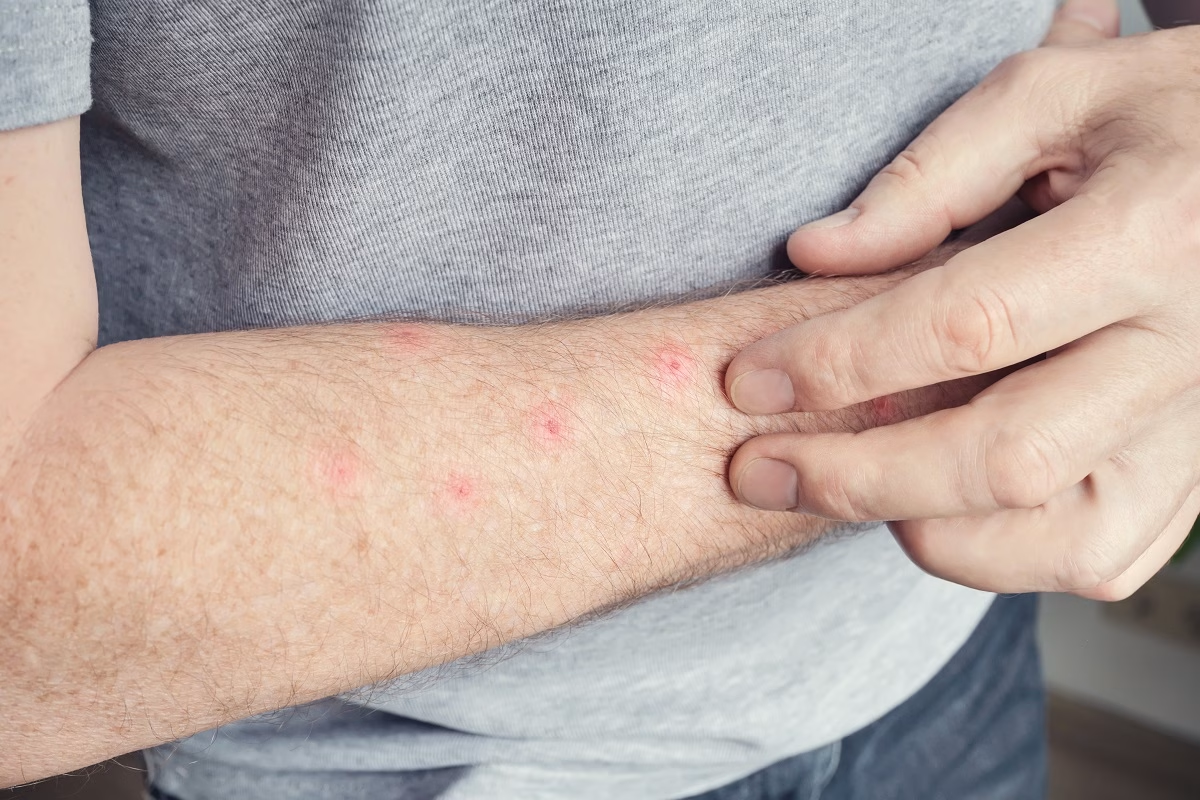
A common allergy that occurs when the immune system overreacts to an antibiotic called Penicillin is called penicillin allergy. Usually, people who develop it experience the following symptoms. For example, skin rash, swelling, and difficulty breathing, but may also experience other symptoms. Sometimes, an allergic reaction can be a medical emergency, which means the affected person requires immediate medical attention.
In other words, this disorder occurs when the immune system reacts negatively to Penicillin or an antibiotic in the Penicillin family (beta-lactam antibiotics). Normally, this medication is used to treat bacterial infections.
It is important to understand that you have developed a penicillin allergy today does not mean it will always occur. For instance, about 80% of people diagnosed with this type of allergy lose their sensitivity to the medicine after 10 years.
Furthermore, penicillin allergy is one of the most common medical allergies, and it affects about 10% of all people in the U.S.
Types of Penicillin
Generally, there are multiple types of Penicillin that come as oral medicines or injections. Check below the most common types of Penicillin:
- Amoxicillin
- Carbenicillin
- Dicloxacillin
- Ampicillin
- Nafcillin
- Oxacillin
- Penicillin G and V
- Piperacillin
- Ticarcillin
Symptoms
Usually, people who develop a penicillin allergy may experience the following symptoms. Check below some examples:
- Swelling around the face, hands, and feet
- Cough
- Nasal congestion
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash or hives (raised pink areas of skin)
Most people develop symptoms within 1 hour after taking Penicillin. Rarely, adults may have symptoms days or weeks after using this antibiotic.
Severe Symptoms
One of the most serious reactions to Penicillin is anaphylaxis. This is a life-threatening allergic reaction that requires medical care. If you suspect someone has anaphylaxis, immediately call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room (ER). Check below for other severe symptoms of penicillin allergy:
- Swelling that affects the whole body
- A sudden drop in blood pressure (hypotension)
- Diarrhea
- Tightness in the chest
- Wheezing
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Lightheadedness or dizziness
- Fast or irregular heartbeat
- Syncope (fainting or loss of consciousness)
Do not hesitate to visit a doctor if any of the previous symptoms occur, especially after taking Penicillin.
Causes
This type of allergy occurs when the immune system overreacts to Penicillin. In normal circumstances, the immunity helps defend the body from invaders (including bacteria, viruses, and other germs) that can make you sick. Thus, penicillin allergy occurs when the immune system mistakenly recognizes this antibiotic as a negative foreign substance.
Moreover, some people may experience this type of allergy after the first time he/she take Penicillin. Other times, it may occur when you administer Penicillin for the second time. However, the immune system has had time to make antibodies for it. Antibodies are proteins made by white blood cells that help defend the body against germs.
Risk Factors
While this allergy can affect anyone, there are some factors that may increase your risk of developing it. For example:
- Hay fever
- Eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis)
- Asthma
- A family history of penicillin allergy
- Previous drug reactions (such as a medical history of side effects to other medicines)
- Other allergies
- Viral infections, including Epstein-Barr virus, human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6), cytomegalovirus (CMV), and others.
- HIV infection
This document does not contain all possible factors that may elevate your risk of developing penicillin allergy.
How to Prevent Penicillin Allergy?
Commonly, it is difficult to know if you are allergic to Penicillin if you have never been tested for it. One of the best ways to prevent this type of allergy is to perform an allergy test. Therefore, you can inform your healthcare professionals about your allergy, so they don’t prescribe a penicillin-type antibiotic.
Diagnosis
Usually, doctors begin the diagnosis of penicillin allergy with an evaluation of the medical and family history and physical examination to check for abnormalities linked to the disease. They may also ask some questions about the symptoms. However, to confirm or rule out this disorder, doctors often perform an allergy test. During this test, physicians will drop two components of Penicillin on the skin every 15 minutes to look for a skin reaction, including skin discoloration, itching, and hives.
However, when this test is negative, doctors may perform another test to make sure you do not have this type of allergy. It is called an intradermal test, and it involves a small needle to place a small amount of Penicillin underneath the skin. The reaction usually occurs within 15 minutes. These may include raised red bumps (such as those caused by a mosquito bite). When both tests are negative, it means you are at low risk for severe or immediate allergic or anaphylactic reactions to Penicillin.
Treatment
Healthcare professionals may prescribe different treatments because they depend on various factors. These include the severity of the allergic reaction, overall health, age, and preferences. Check below some treatments often recommended for people with penicillin allergy:
- Stopping the use of Penicillin
- Antihistamines (a group of medicines used to reduce allergic reaction symptoms)
- Prescribed corticosteroids to treat severe swelling, inflammation, or itching
- An Epinephrine injection for severe anaphylaxis (if you are at increased risk of anaphylaxis, you should have this Epinephrine shot with you all the time)
Are There Different Antibiotics Available if I am allergic to Penicillin?
When allergy tests are positive, doctors prescribe other types of antibiotics. These include:
- Tetracyclines (such as Doxycycline)
- Clarithromycin
- Ciprofloxacin
- Gentamicin
- Vancomycin
In some cases, there are no other antibiotics that are a safe and effective alternative. Thus, physicians may recommend drug desensitization therapy. During this treatment, you will take a small amount of the medicine and then gradually increase the dose. This therapy is often performed under medical supervision to prevent severe adverse reactions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How soon after treatment will I feel better?
Commonly, people feel immediate relief from some symptoms right after starting the treatment. In most cases, it takes several weeks for a skin rash and hives to clear up.
Can I ever take Penicillin again if I have an allergy?
Generally, all people with this type of allergy are able to take it again later in life. However, it is advised to perform allergy tests before using it again to prevent an allergic reaction. Other times, physicians may recommend desensitization therapy to begin taking Penicillin safely.
Is a penicillin allergy genetic?
This type of allergy is not genetic. It means you cannot inherit it even if you have a family history of the same allergy. Ask your healthcare provider if you have any other questions.