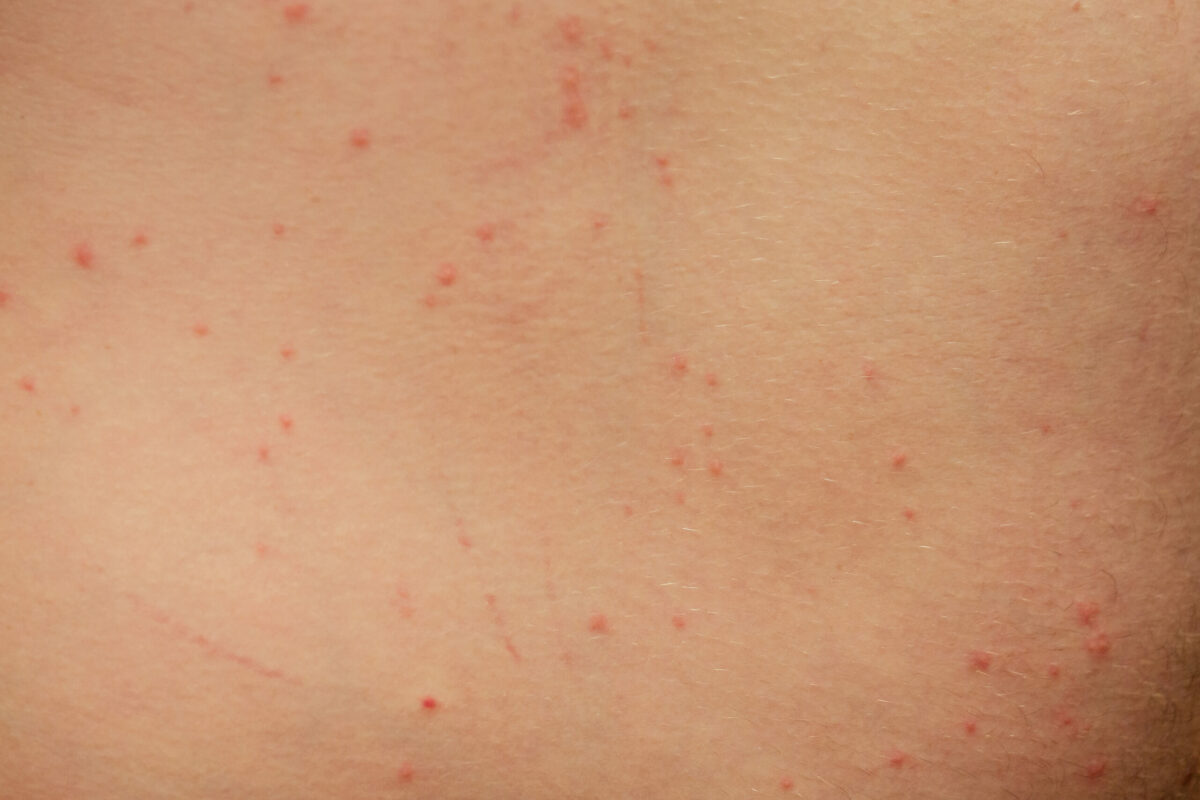
A skin condition that occurs commonly and causes hair follicles to become inflamed is called folliculitis. In most cases, it appears due to bacterial infection. In the beginning, it may look like small pimples around small pockets where each hair grows (also known as hair follicles).
However, this condition may be itchy, sore, and embarrassing and infection may spread and turn into crusty sores. In mild cases, it goes away on its own without leaving scars or requiring treatment within several days. In any case, some people may experience a more severe form of folliculitis that needs prescription medicines. If the condition is not treated it may lead to permanent hair loss and scarring.
There are some folliculitis types known as hot tub rash and barber’s itch.
Symptoms
People with folliculitis usually notice the following symptoms. Examples include:
- Burning and itchy skin
- Inflamed bumps
- Painful and tender skin
- Pus-filled blisters that may break and crust over
- Clusters of pimples or small bumps that surround hair follicles
If you do not know how to manage these symptoms, contact your healthcare professional.
Folliculitis Types
The primary types of this condition can be superficial or deep. While the superficial type involves the follicle part only, the deep type affects the entire follicle and usually, it is more severe. Check below folliculitis types:
- Bacterial folliculitis – It causes a rash of puss-filled bumps that is itchy and it is the most common folliculitis type. Commonly, it happens when hair follicles are infected with a bacterial called Staphylococcus aureus (staph). This is a bacteria that lives on the skin all the time and often causes problems when it enters the body through cuts or wounds.
- Pseudomonas folliculitis (hot tub rush) – This type occurs due to pseudomonas bacteria usually found in hot tubs, water slides, and heated pools where pH and chloride levels are not within normal ranges. It causes symptoms within 48 hours after exposure and you may notice a rash of round itchy bumps.
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae (razor bumps) – It looks like folliculitis but happens due to ingrown hairs while follicles are not infected. Commonly, it appears in people with curly hair who shave close. The symptoms usually appear on the neck and face.
- Pityrosporum folliculitis – It happens due to a yeast infection and symptoms such as pus-filled bumps appear often on the chest and back.
Check below additional types:
Gram-negative Folliculitis
In such cases, pus-filled bumps appear around the mouth and nose. Sometimes, this folliculitis type appears in people who follow a long-term treatment for acne with antibiotics.
Eosinophilic Folliculitis
Intense itching and recurrent patches of bumps and pimples that appear near hair follicles on the face and upper body cause this type of folliculitis. Commonly, eosinophilic folliculitis happens in people with HIV/AIDS. However, more research is needed because experts do not fully understand the cause of this folliculitis type.
Boils (furuncles) and Carbuncles
It happens when follicles become deeply inflamed with staph bacteria. The symptoms such as a painful inflamed bump appear usually suddenly. Additionally, a cluster of boils is called a carbuncle.
Sycosis Barbae
Commonly occurs in people who shave.
If the condition is widespread or symptoms last more than 2 weeks, immediately contact your doctor. You may need antibiotics or antifungal medications to control the condition. Seek emergency help if you experience a sudden increase in pain or redness, fever, chills, and malaise.
Causes
This condition occurs when hair follicles become inflamed due to bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus or staph is the most common cause of this folliculitis). However, it may also occur due to viruses, parasites, fungi, physical injuries, or medicines. Rarely, the exact cause of folliculitis cannot be identified.
Risk Factors
This condition can occur in anyone and the following factors increase the risk of developing it. Examples include:
- Wearing clothes that block heat and sweat regularly. These include rubber gloves, high boots, and others.
- Soaking in a hot tub, whirlpool, or public pool without proper maintenance.
- Damage to the hair follicles through waxing, wearing tight clothes, hair styling practices (such as wigs, oils, and traction), or shaving.
- Certain medicines including corticosteroids (such as Prednisone), long-term antibiotic use, some chemotherapy drugs, and others.
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating)
- Dermatitis
- Chronic health conditions (including diabetes, HIV/AIDS, and others)
What are the Potential Complications of Folliculitis?
Those who experience this condition may also notice some complications. Examples include:
- Recurrent infection
- Permanent scarring
- Hyperpigmentation (dark patches on the skin) or hypopigmentation (lighter patches than usual) but these complications usually last a short period.
- Permanent hair follicle damage and hair loss
How to Prevent Folliculitis?
The following tips may help prevent or avoid folliculitis. Examples include:
- Regularly wash your skin and do not share your towels
- You should protect your skin against friction, especially if you are more likely to develop folliculitis. Usually, the friction is caused by helmets, tight clothes, and backpacks.
- Regularly do laundry, especially oil-soaked uniforms
- Dry rubber gloves every time between uses
- It is advised to use hair-removing products (such as depilatories) or other hair-removal methods. However, they also may irritate the skin the risk of folliculitis is lower.
- Underlying conditions – Some people experience folliculitis due to certain conditions such as hyperhidrosis. Therefore, you should consult your doctor for treatment or you can consider the following tips. For example bathing daily, using antiperspirant, and changing regularly sweaty clothes.
- According to the CDC, you should use clean hot tubs and heated pools only. Otherwise, you are at higher risk of developing folliculitis.
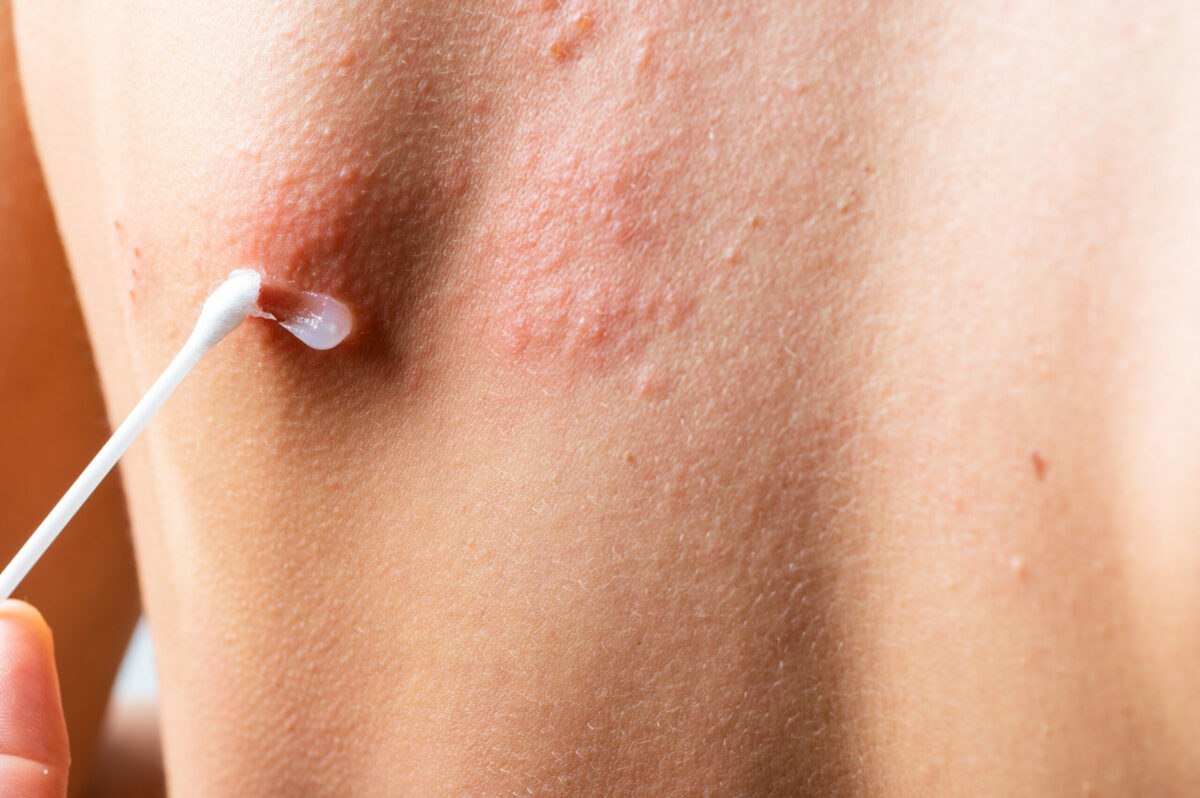
- Consult with your healthcare professional if folliculitis occurs frequently. Physicians may recommend some prescription antibacterial medicines (such as ointments). You can also wash your body with Chlorhexidine.
Shave
It is not recommended to share frequently, especially if you experience facial folliculitis. One way to reduce the frequency of shaving is to grow a beard. Moreover, check below some tips that may help control the symptoms if a beard is not an option for you:
- Shave less commonly
- Regularly wash your skin with warm water and use a mild facial cleanser, especially before shaving
- Apply more shaving lotion before shaving and do not forget to apply a moisturizing lotion after shaving.
- Do not share your razors, towels, or washcloths
- Shave in the hair growth direction
Diagnosis
In most cases, to diagnose this condition, doctors perform a physical examination only. During this procedure, they check the skin for folliculitis symptoms. However, doctors may ask you some questions about your medical history.
Treatment
The treatments that doctors prescribe for folliculitis are different because depend on several factors including the type and severity of the condition, using over-the-counter medicines, and others. Sometimes, people need to go to a dermatologist for prescription medicines because other options do not work. A dermatologist may help you control the condition, identify a medicine that may cause symptoms, prevent damage and scarring of the skin, or make scars less noticeable. Check below some treatment options usually recommended by doctors:
Medicines
- Medicines to calm inflammation – These include creams and pills that help reduce inflammation in people with mild eosinophilic folliculitis. Moreover, your doctor may prescribe an antiretroviral therapy that helps lessen the eosinophilic folliculitis symptoms in people with HIV/AIDS.
- Antifungal medicines – This group of medications is used to treat folliculitis caused by yeast infection. These include creams, shampoos, and pills.
- Antibiotics – These medicines are prescribed by doctors when infection occurs due to bacteria. The medicines used for folliculitis come in different forms including gels, pills, and lotions.
Other Treatment Options
- Surgery – This procedure is usually prescribed by doctors for people with a large boil or carbuncle. During surgery, doctors will cut it to drain the pus, which helps lessen pain, speed recovery and prevent complications (such as scarring).
- Laser hair removal – It is usually recommended by doctors for people with pseudofolliculitis barbae and when other treatment options are not effective. Possible adverse reactions to this procedure include scarring of the skin, hypopigmentation, and hyperpigmentation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common cause of folliculitis?
Mostly, it occurs when hair follicles are infected with bacteria (usually Staphylococcus aureus also called staph). However, this condition may occur due to other causes including fungi, parasites, viruses, medicines, and others.
What health conditions may be mistaken for folliculitis?
These include:
- Acne keloidalis nuchae
- Keratosis pilaris
- Scabies
- Hidradentis suppurativa
- Papulopustular rosacea
- Acne vulgaris
Do not take any medicines or supplements if you experience folliculitis symptoms and go to a doctor for diagnosis.
What happens if folliculitis is left untreated?
If you ignore the symptoms and do not get treatment, you may notice some complications because it may result in deep infections. As a result, you may experience permanent scarring, cellulitis, or even the infection may enter the bloodstream and become life-threatening. Ask your healthcare provider if you have additional questions.