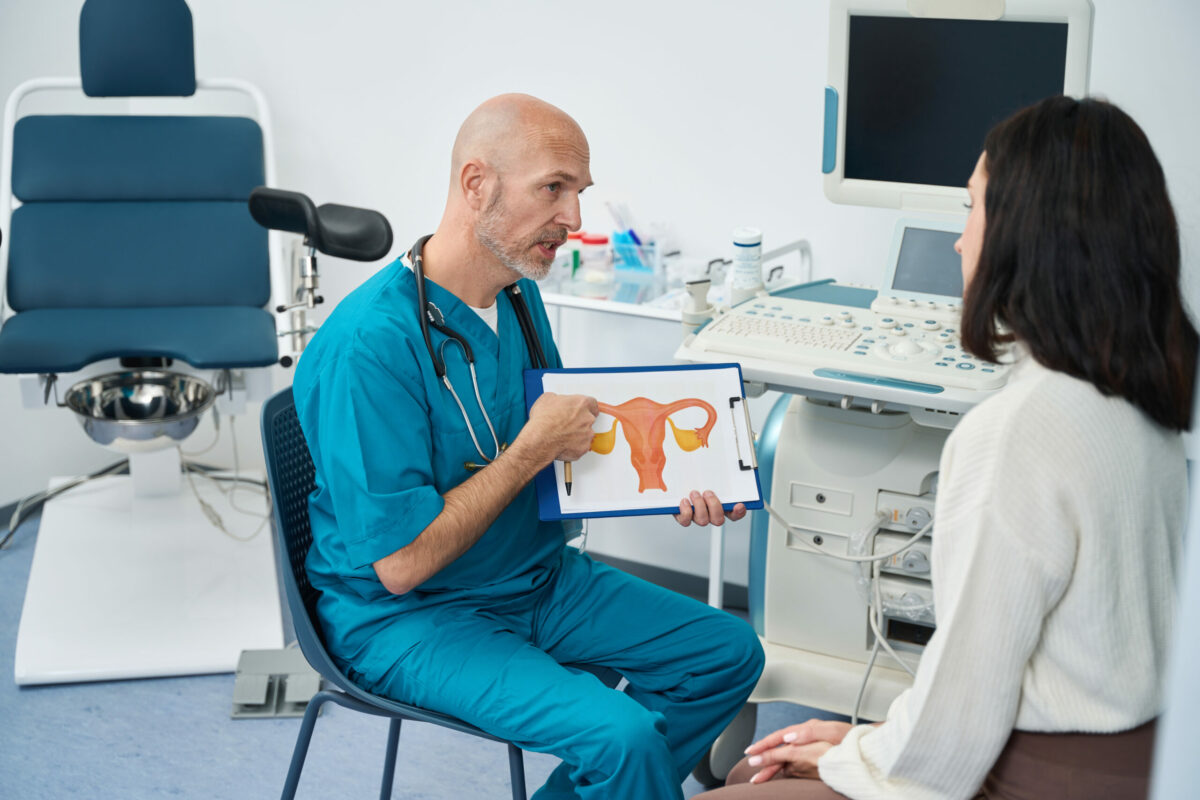
This is a common health condition, in which tissue similar to the lining of the uterus begins to grow in other places including within the abdomen and pelvic area. Endometriosis can negatively affect your daily life and provoke painful and heavy periods and fertility problems.
What is Endometriosis?
The inner part of your uterus is called the endometrium and when the same tissue grows in other parts can cause some unpleasant symptoms. Additionally, during the menstrual cycle, this tissue usually becomes inflamed because it is hormonally sensitive. Therefore, these growths can also cause ovarian cysts, lesions, deeper nodules, adhesions, scar tissue within your body, and other unpleasant outcomes. Check below some places where endometriosis can develop:
- Fallopian tubes
- Ovaries
- Vagina
- Peritoneum (it is the lining tissue of your abdomen and pelvis)
- Bladder and ureters
- Intestines
- Rectum
- Diaphragm (a muscle that plays an important role in breathing)
- Outside and back of your uterus
In case you suspect you have endometriosis, see a doctor for a check-up.
Risk Factors
There are some risk factors that may elevate your risk of developing this health condition. Examples include:
- Certain defects in your uterus or fallopian tubes
- The duration and length of your menstrual cycle
- Females who start having periods before 11 years old may be at higher risk
- Family history of endometriosis
Is Endometriosis a Genetic Condition?
However, the exact cause of this disease is not clear, experts noticed a connection between family history and an increased risk of developing endometriosis. It is recommended to consult with your physician about your risk if your mother, grandmother, or sister has this disease.
Symptoms
A wide variety of symptoms associated with endometriosis may appear and the primary symptom is pain, which can be mild to severe. A person who experiences this condition usually feels pain in the abdomen, pelvic region, and lower back. Some people do not know they have endometriosis until they perform an investigation of infertility. Check below some symptoms that a person with endometriosis experiences:
- Severe painful menstrual cramps
- Pain during sex
- Abdominal or back pain during or between periods
- Problems becoming pregnant (infertility)
- Painful bowel movements
- Heavy bleeding during menstrual periods
In addition, the intensity of symptoms does not have a connection with the severity of endometriosis. It means that some people with mild endometriosis can experience severe pain and someone with mild endometriosis may experience mild pain.
For those who experience this condition, the first symptoms will be pain felt in the abdomen, pelvic area, and lower back. Moreover, menstrual periods can be heavier than usual.
Causes
The exact cause of this disease is now known but when you have this condition, some similar tissue grows to the lining of your uterus and usually causes pain. However, if these additional tissues grow outside of your uterus, it may lead to adhesions (scar tissue).
Diagnosis
Usually, pain and heavy periods and the symptoms that make you consult a doctor. Thereafter, healthcare providers will ask about symptoms, previous pregnancies, family history, and others. They may also perform a pelvic exam. For more details, your doctor may perform imaging using ultrasound. In case it is not enough physicians may perform MRI and laparoscopy alongside previous tests to diagnose this condition. During laparoscopy, the surgeon can look inside your body using a tiny camera called a laparoscope. An additional test can be a biopsy. It involves a small sample of tissue that will be sent to the laboratory.
There are some cases when endometriosis is found accidentally, which means that not all females who experience this condition notice any symptoms.
Treatment
Doctors will prescribe a treatment based on the severity of your condition and symptoms, age, and plans for future pregnancies. As a result, the treatment focuses on symptoms of endometriosis and fertility problems by surgery and medicines. Drugs are used to keep under control symptoms and include pain drugs and hormonal therapies.
Hormonal Therapies
- Danazol – This is a hormonal medicine that blocks the production of the hormones that provoke menstrual periods. Using this medication for endometriosis symptoms, your menstrual periods may stop at all.
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) Medicines – This is another medicine used to stop menstrual periods and relieve pain.
- Birth Control – This form of hormonal treatment includes estrogen and progesterone that comes in different forms such as vaginal rings, birth control shots, tablets, implants, or IUDs that help to have less painful periods. This hormonal option is not for women that planning a pregnancy.
However, you should not use any of these hormonal options without a physician’s recommendation. In addition, you should know that symptoms may return if you stop using these medicines and avoid using them if you are planning to become pregnant.
Medicines used to lessen pain usually are nonprescription pain relief medicines and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
In certain circumstances, your physician may advise surgery to treat endometriosis. However, it is usually used when medicines alone are not enough and you see no improvements in your disease. In any case, this health condition is considered a chronic disease and its symptoms may return even after surgery. That’s why commonly physicians recommend surgery alongside medicines. Both used at the same time can improve the treatment outcome. Check below some surgical options:
- Hysterectomy – This procedure is usually done in severe cases of endometriosis. This surgery involves the removal of your uterus and present scar tissue. Discuss with your doctor about your desire for future fertility.
- Laparoscopy – In this surgery option, the surgeon will cut about 1 centimeter in your abdomen. Thereafter, will insert the tool called laparoscope. It is used inside your body to determine endometriosis and remove lesions.
Discuss with your healthcare professional for more details.
In some cases, endometriosis can disappear on its own, which usually happens after menopause due to decreased estrogen production. However, for many females, this condition requires continuous treatment to control symptoms such as pain. Therefore, it is advised to have regular appointments with your physician.
Complications
You should not leave this health condition untreated even if you do not have any symptoms because it may lead to certain complications. For example cysts, scar tissue, chronic long-term pain, heavy menstrual periods, and others. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent future unwanted outcomes. In addition, problems with becoming pregnant also may occur if you ignore this disease.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is possible to prevent endometriosis?
There are some tips that may help to decrease the risk of developing endometriosis. For example:
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Starting your menstrual periods at a later age
However, you may experience this condition anyway because there may be some genetic reasons.
Can endometriosis provoke cancer?
The risk that this condition will cause cancer (epithelial ovarian cancer) is very low. Discuss with your healthcare professional for more details.
Who can get endometriosis?
This condition usually affects people aged from 25 to 40 years old. However, some women can still search for relief even after menopause due to discomfort and pain. If you think you have endometriosis, contact a healthcare professional right away.