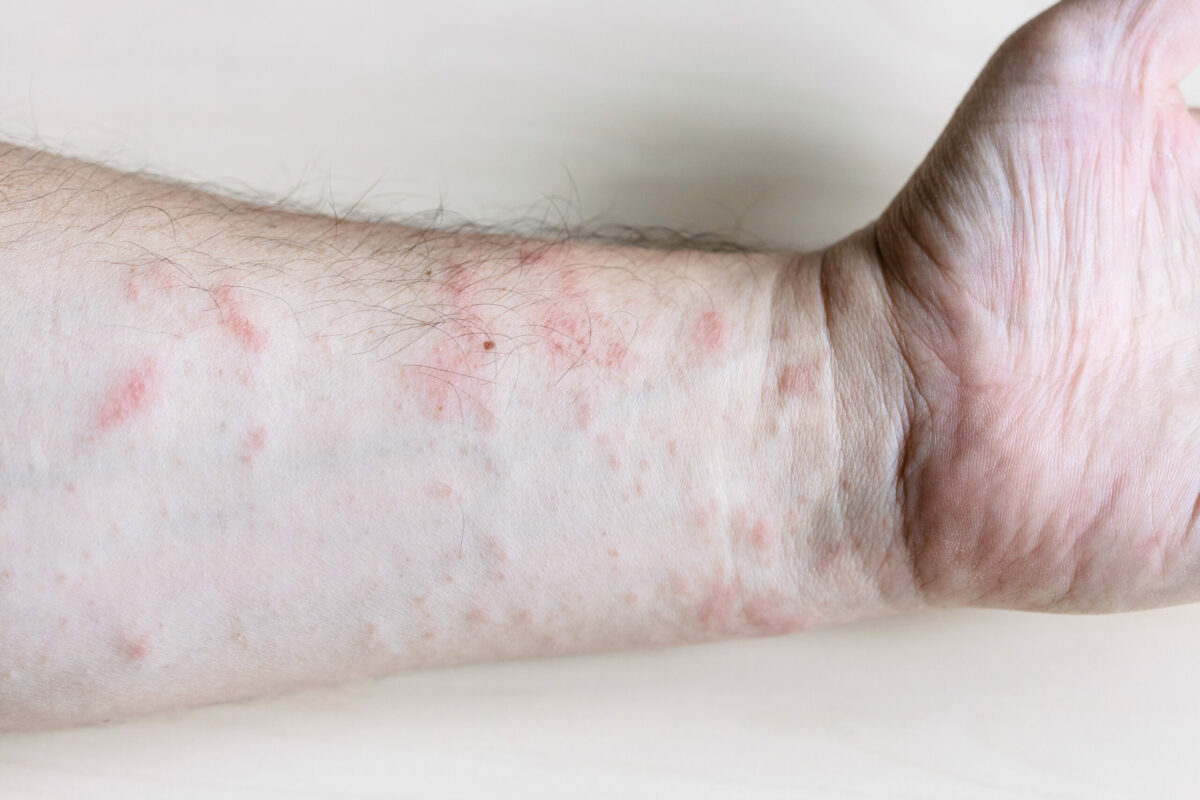
A skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and inflamed skin is called atopic dermatitis (eczema). It usually appears in young children but may occur at any age as well. Moreover, this is a chronic (long-lasting) skin disease that tends to flame at times. It also can be irritating but it is not a contagious skin disease.
Physicians recommend regular moisturizing and other skin care habits to prevent new flares (outbreaks) and itching. When moisturizing is not enough, doctors may prescribe some medicines (such as creams and ointments).
Symptoms
The symptoms of this skin disease may appear anywhere on the body and usually are different among people. Check below some eczema symptoms:
- Crusting and oozing
- Sensitive and raw skin due to scratching
- Pruritus (itchiness)
- Rash
- Cracked and dry skin
- Over time the skin around the eyes may darken
- Thickening of the skin
- Small and raised bumps on Black or brown skin
Mostly, eczema starts before 5 years old and may continue into teen years and adulthood. In some people, this condition flares and then disappears for a period (in some cases for a few years).
Do not hesitate to visit a doctor if you notice your child has atopic dermatitis symptoms. In addition, if your child experiences fever and the rash looks infected, seek emergency care.
Causes
Sometimes, the condition occurs due to a gene change (mutation) that negatively affects the skin’s ability to provide protection. As a result, the weak barrier function of the skin leads to dryness and decreased ability to protect against bacteria, irritants, allergens, and other environmental factors (including tobacco smoke).
Other people may experience atopic dermatitis due to an increased amount of bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus) on the skin.
In rare cases, weakness of the protective barrier may occur due to an immune system reaction that causes inflammation of the skin and other symptoms.
While eczema is one dermatitis type, there are other common skin conditions such as contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis (dandruff).
Risk Factors
One of the strongest risk factors for eczema is an FLG gene mutation (change). This gene provides the production of profilaggrin, which is needed to make a protection barrier against bacteria, allergens, and toxins. However, people who have a family history of dermatitis also are at increased risk of developing this skin condition.
What Are The Possible Complications of Atopic Dermatitis?
People with eczema may experience certain complications, especially if they do not get treatment or experience a severe form of the disease. Examples include:
- Asthma and hay fever – These complications are common among people with eczema and can occur either before or after developing this skin disease.
- Food allergies – People with atopic dermatitis frequently develop food allergies and one of the primary symptoms of this condition is urticaria (hives).
- Chronic itchy and scaly skin – This is a condition called neurodermatitis (lichen simplex chronicus) and it makes the skin become discolored, thick, and leathery.
- Post-inflammatory hypo- or hyperpigmentation – This complication usually appears after the rash has healed and causes certain patches of the skin to appear darker or lighter.
- Skin infections – Frequent scratching of the skin that causes cracks and open sores on the skin may increase your risk of developing bacterial and viral infections. However, sometimes, these infections may spread and become life-threatening.
- Irritant hand dermatitis – It often happens in people who frequently use harsh soaps, detergents, and disinfectants at work.
- Heart disease – When a severe form of atopic dermatitis occurs, the risk of developing heart problems increases significantly. These include heart failure, stroke, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, and others.
- Allergic contact dermatitis – This is one of the most common complications in people with eczema. This condition causes an itchy rash when you come in contact with certain substances you are allergic to.
- Insomnia – Persistent itching that happens in people with atopic dermatitis may cause sleeping disturbances.
- Mental health problems – Depression and anxiety are common in people with this dermatitis type due to persistent itching and sleeping problems.
How to Prevent Atopic Dermatitis?
Check below some tips that may reduce the symptoms of this skin disease and prevent flares:
- Regularly moisturize your skin by using creams, ointments, shea butter, lotions, and other products.
- It is advised to take warm baths (not hot) every day and limit either shower or bath to roughly 10 minutes.
- It is recommended to choose a cleanser that is free of fragrances, alcohol, and dyes. Furthermore, for young children, the only you need to clean them is warm water.
- After bathing, you should gently pat the skin with a soft towel and apply the moisturizer (preferably within 3 minutes).
What are Triggers of the Atopic Dermatitis?
The triggers are different among people and you should try to find and avoid them. Generally, everything that causes an itch may trigger an eczema flare. Check below the most common atopic dermatitis triggers:
- Skin infection
- Dry and cracked skin
- Rough wool fabric
- Stress
- Heat and sweat
- Cleaning products
- Pet dander
- Dust mites
- Mold
- Pollen
- Tobacco smoke
- Fragrances
- Other irritating chemicals
Some children and infants may have flares due to certain foods (such as eggs and cow’s milk). Discuss with your healthcare professional about ways to find food allergies.
Diagnosis
Doctors usually diagnose this condition by performing a physical examination and questions about your medical history and symptoms. Sometimes, they may perform additional tests to confirm the condition and exclude other diseases that cause similar symptoms.
Patch Testing
This test involves small amounts of multiple substances that are applied to your skin and after that covered. After several days, your doctor will remove these coverings to see for signs of a reaction. This is an effective test to determine allergies that cause the dermatitis.
Treatment
Commonly, the eczema treatment begins with moisturizing and self-care habits. Physicians usually recommend medicines that help to control itching and repair skin when self-care habits are not enough.
In some cases, it is quite difficult to control the condition and you may try multiple treatment options to find the best one. However, this condition may return even if the treatment is successful.
Medications
- Topical medicines – These medications come in multiple forms and doses (such as creams, ointments, lotions, and gels). Commonly, physicians recommend corticosteroids, and calcineurin inhibitors (such as Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus).
- Antibiotics – This group of medications is usually recommended by doctors when you experience skin infections.
- Medications to reduce inflammation – People who experience a severe form of eczema may need medications to lessen inflammation and control the symptoms. In most cases, physicians recommend Prednisone, Methotrexate, Cyclosporine, and Azathioprine.
- Other medications – Doctors may also recommend certain injectable biologics (monoclonal antibodies) such as Dupilumab and Tralokinumab to control the symptoms in people with moderate or severe atopic dermatitis. These medicines are usually recommended when other treatments do not work.
Therapies
- Wet dressings – This is an intensive treatment for severe eczema and involves applying a corticosteroid ointment and then wrapping it with a wet gauze topped with a layer of dry gauze.
- Light therapy – It is usually used in people who do not get better after topical medications or flare again quite fast after treatment. It involves exposure of the affected area to the natural sunlight. However, other forms also are available. These include artificial ultraviolet A (UVA) and narrow-band ultraviolet B (UVB). In any case, you should not use this therapy for long periods because it may cause certain adverse reactions including premature skin aging, hyperpigmentation, and an increased risk of skin cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of atopic dermatitis?
While the exact causes of eczema are not known, experts believe that a combination of factors causes this condition. These include genetics, environmental factors, skin barrier changes, environmental factors, and others. For more details, discuss it with your healthcare professional.
What are the most common symptoms of eczema?
These include:
- Rash
- Dry skin
- Persistent itching
- Skin darkening
- Raw skin
- Oozing and crusting
- Bumps
If any of the previous symptoms occur, do not hesitate to see a doctor.
Can dermatitis cause heart problems?
As per studies, people with severe atopic dermatitis are at increased risk of developing heart complications. These include heart attack, angina, heart failure, cardiovascular death, atrial fibrillation, and others. If you have additional questions, ask your healthcare provider.